1 Using generative AI in web apps
Generative AI web apps weave large language and media models into everyday interfaces to produce text, images, audio, and video on demand, enabling personalized, conversational, and adaptive experiences that go far beyond static logic. This chapter sets expectations for building such systems in production, assuming basic JavaScript and React familiarity and then guiding you through React, Next.js, and the Vercel AI SDK, with models from providers like Google AI and OpenAI. Through focused projects—culminating in a voice-driven interview assistant and a RAG-powered knowledge system—you learn practical patterns for integrating models, tools, and external data securely and reliably, all with the goal of empowering you to ship real, working AI features.
It surveys what generative AI can do in web contexts—text and code generation, image and multimedia creation, content enhancement, creative exploration, and complex problem solving—then grounds those capabilities in concrete scenarios such as digital marketing toolkits, customer-support chat and feedback workflows, and adaptive mock interview agents with speech-to-text. You also get a clear view of how an AI web app works end to end: users interact through traditional or conversational UIs; backends orchestrate preprocessing, model selection, and calls to internal or external APIs; models generate responses; and results are streamed back with optional feedback loops. Under the hood, caching, containerization, serverless tasks, model-serving frameworks, and careful deployment and scaling strategies keep latency low, costs predictable, data safe, and uptime high.
Finally, the chapter maps the evolving ecosystem and key design choices. It explains why React, Next.js, Vercel AI SDK, and LangChain.js pair well for rapid development and provider flexibility; how to choose between providers and model families (transformers, autoregressive models, GANs, VAEs, and legacy RNNs); and when to rely on pre-trained APIs versus self-hosted models. It contrasts traditional discriminative AI with generative approaches made practical by transformers and self-attention, and it addresses real-world constraints: accuracy and quality control, performance and cost, security and misuse, regulatory compliance, bias mitigation, and user experience. Practical techniques—clear objectives and context framing, parameter tuning, validation and auditing, streaming responses, and multimodal inputs—help you deliver reliable, accessible AI features that users trust.
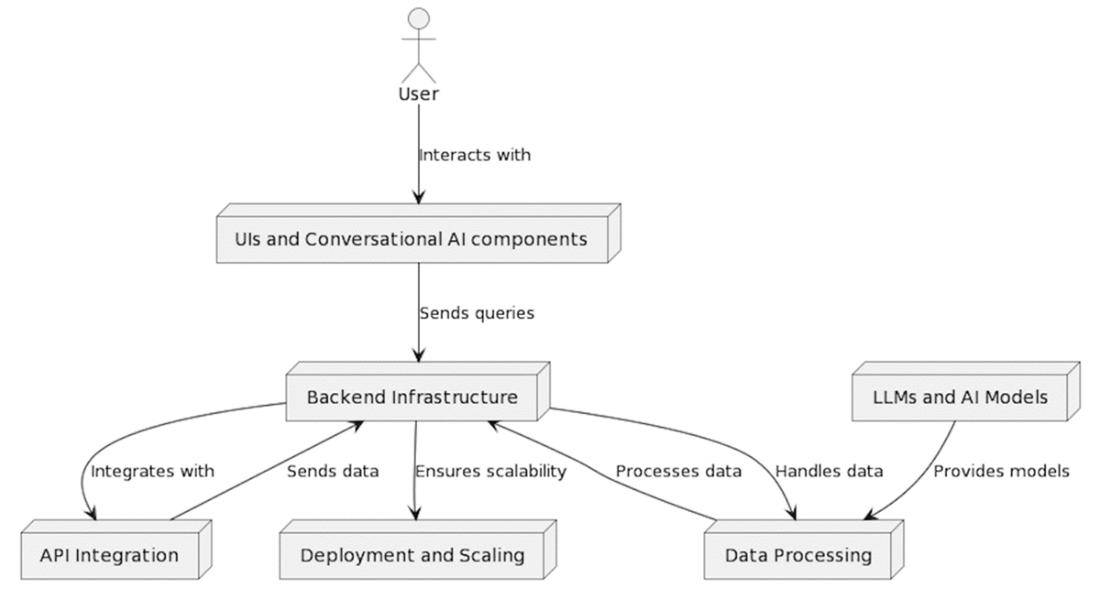
The flow of information and interactions between the key components of a generative AI web application.
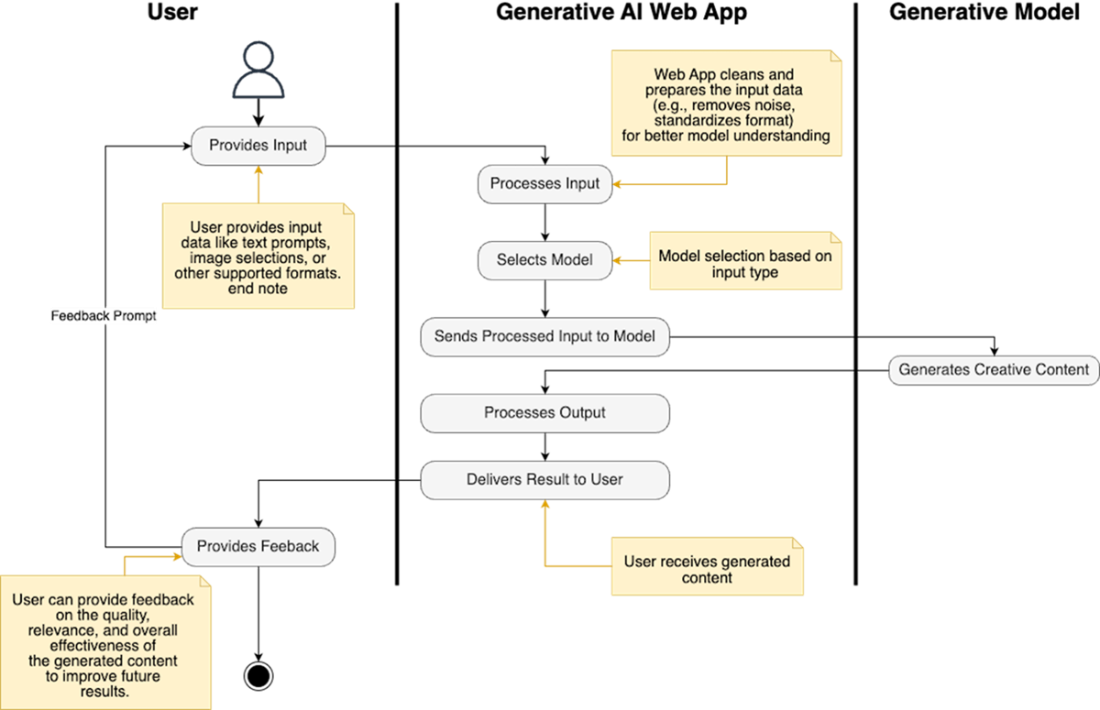
How an AI web app works: users input data, the app processes it, selects a model, generates content, delivers it, and optionally collects feedback.
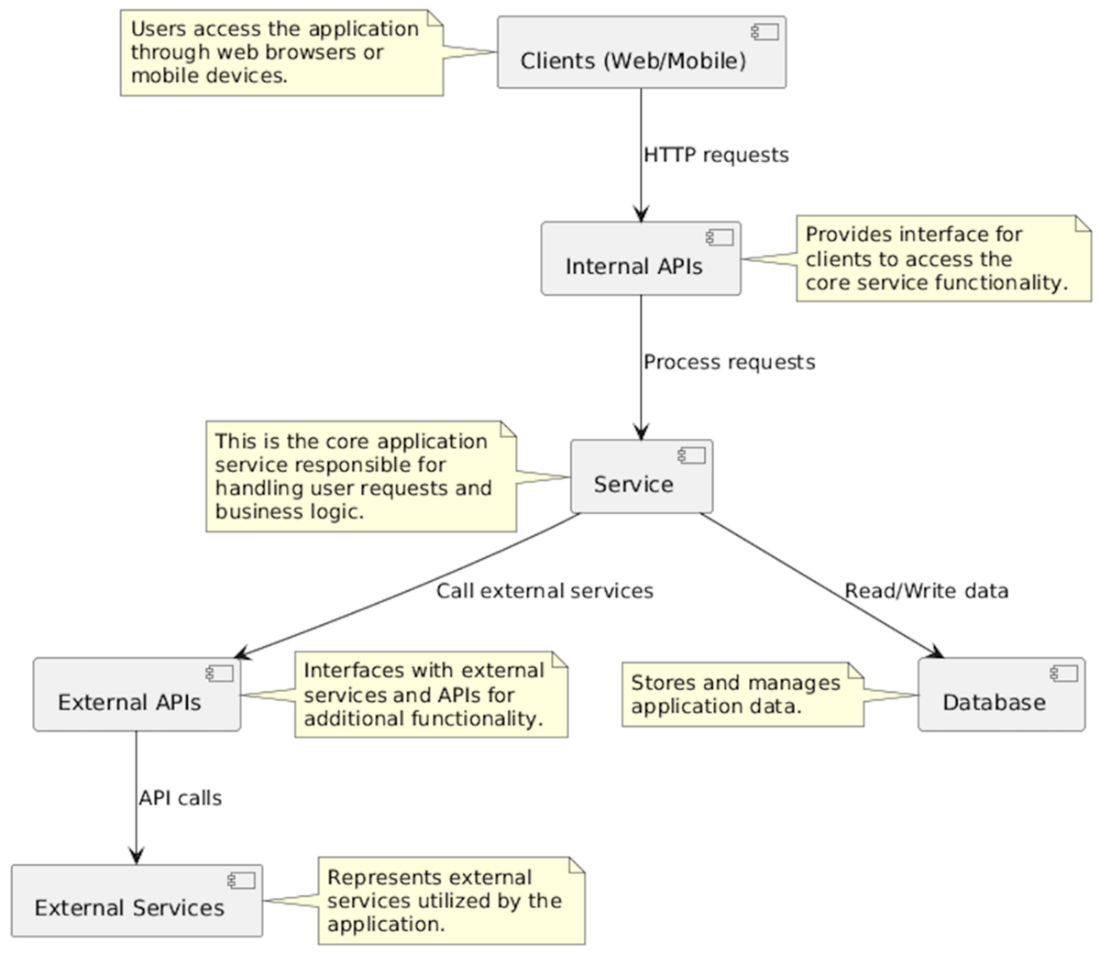
Simplified architecture diagram of a web application ecosystem. Clients, including web browsers and mobile devices, interact with the core application service, which handles user requests and business logic. The service interacts with a database to store and manage application data. Additionally, the service communicates with external APIs to access additional functionality and interacts with external services utilized by the application.
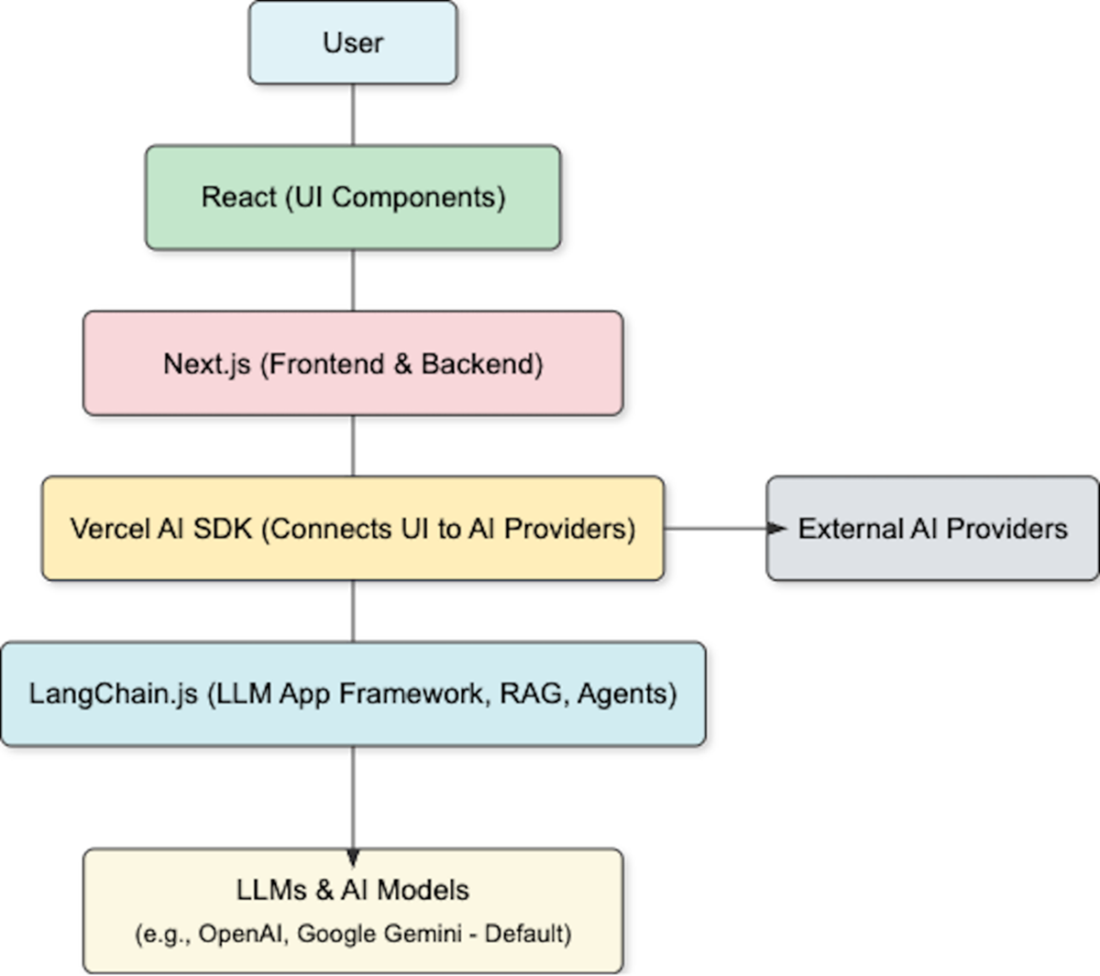
Leveraging key technologies to create generative AI web applications
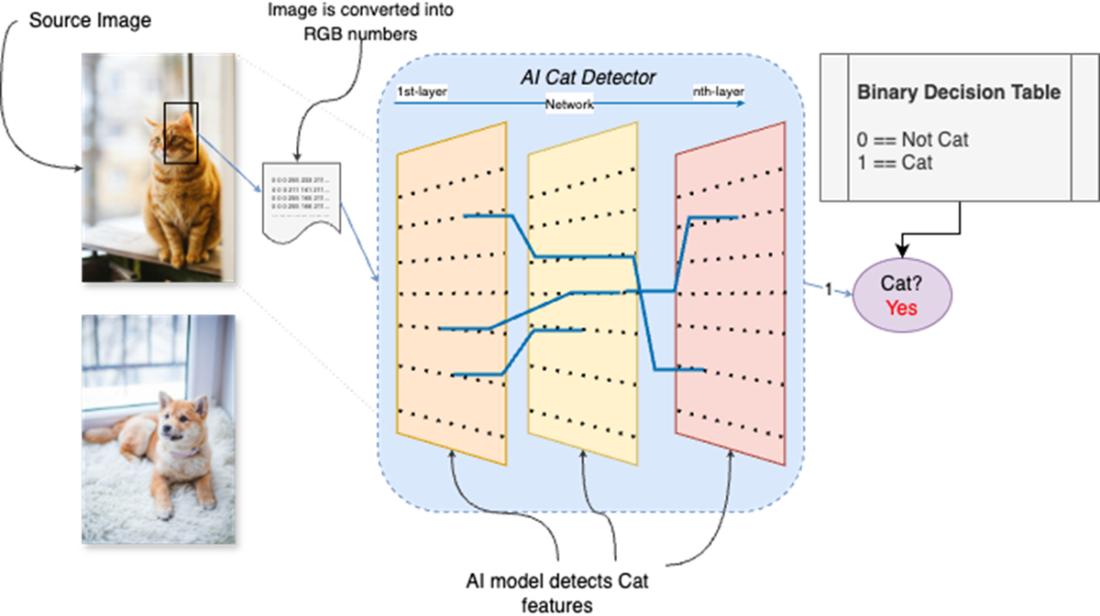
How AI can be used to detect whether a picture of a cat is a cat or not. It accepts an image as input and responds with yes or no (or 0 and 1).
Summary
- Generative AI can generate not only text, but all sorts of media resources like images, video clips and audio. This greatly enhances their potential usage in web applications, and real-world uses of generative AI in web applications range from digital marketing and customer experience management to mock interview applications.
- Generative AI web apps center on powerful models like large language models (LLMs) to create content from user input. The apps require a full supporting ecosystem to integrate with the model, including UI and conversational AI components, backend infrastructure, data processing pipelines, API integration, and deployment and scaling mechanisms.
- The apps we build in this book will use JavaScript and React to display the UI interface components, along with Next.js and the Vercel AI SDK to manage the backend and interact with external AI service providers.
- Choosing the right model for an app is a key architectural decision and depends on the task required. Different model types ( such as LLMs, GANs, autoregressive, transformers, VAE, and RNNs) excel at different kinds of problems. But the model architecture is just one consideration; developers also need to consider the quality and type of data it was trained on.
- Software engineers have been using AI long before generative AI came into existence. Common applications include machine learning, search recommendations, chatbots and computer vision.
- Foundational research like Google's "Attention is All You Need" laid the groundwork for transformative technologies such as transformers, which simplified natural language processing tasks by leveraging attention mechanisms. Transformers revolutionized language modeling by improving efficiency and accuracy in understanding textual data, addressing long-standing challenges faced by traditional AI models.
- Limitations of generative AI include quality control issues, resource intensiveness, security concerns, and regulatory compliance. Concerns include its potential impact on jobs, the reliability of outputs, handling bias, and enhancing the user experience.
FAQ
What is a generative AI web app, and what can it do?
A generative AI web app integrates advanced models—often large language models (LLMs)—to create original text, images, audio, or video. This enables personalized, adaptive, and conversational experiences such as content generation, intelligent automation, and interactive assistants. Typical capabilities include text and code generation, image and multimedia creation, content enhancement, problem solving, and exploratory learning.
Which real-world use cases does the chapter highlight?
- Digital marketing: Toolbox for text-to-image, image-to-image, and prompt-based creative assets using models like DALL·E or Stability tools.
- Customer experience: Generative chatbots for support, sentiment analysis, and personalized responses.
- Mock interviews: AI interviewer agents with real-time feedback and speech-to-text, plus adaptive difficulty and scenario generation.
How does a generative AI web app work from user input to response?
- User input: A prompt, selection, image, or other data is submitted via the UI.
- Backend processing: The app cleans and preprocesses input, performs feature extraction, and selects an appropriate model.
- Content generation: The chosen model (potentially with RAG or other techniques) produces output via internal or external APIs.
- Response delivery: The UI renders results and may capture feedback to refine future responses.
What technologies and frameworks does the book use to build these apps?
- React for UI components and accessibility/performance-minded interfaces.
- Next.js for server-rendered pages, data fetching, and backend integration.
- Vercel AI SDK for provider-agnostic AI integration, state handling, and UI/AI abstractions.
- LangChain.js for conversational chains, agents, and RAG workflows (with LangSmith/LangGraph in the ecosystem).
- Models/providers: Primarily Google Gemini, with occasional OpenAI usage. Later, MCP is used to access tools/data securely.
How do I choose the right model and provider?
Match the model to the task and your data. Assess alignment between model training data and your domain, evaluate latency/cost, and consider modality.
- Model types: LLMs (text), GANs (image-to-image), autoregressive (sequences like text/code/music), transformers (context-heavy tasks), VAEs (anomaly/variations), RNNs (smaller sequential tasks).
- Providers: The chapter uses Google AI (Gemini) and OpenAI; choose based on features, cost, and integration fit.
Should I use pre-trained APIs or host my own models?
- Pre-trained APIs: Fast to adopt, minimal infrastructure, but less custom control.
- Self-hosted: Maximum control and customization, but requires significant compute, ML expertise, and ops maturity.
The book opts for pre-trained APIs (e.g., Gemini, OpenAI) for practicality.
What performance and scaling considerations should I plan for?
- Latency and cost: Choose models that meet interaction speed and budget goals.
- Caching: Use Redis/Memcached to reduce repeated inference costs and latency.
- Compute orchestration: Containerize with Docker; scale via Kubernetes.
- Serverless tasks: Offload specific AI calls to AWS Lambda/Cloud Functions.
- Model serving: Consider TensorFlow Serving, NVIDIA Triton, or Vertex AI for efficient inference.
- UI and data flow: Design clear inputs/outputs; plan pre- and post-processing paths.
How is generative AI different from traditional AI?
Traditional AI often classifies or predicts (e.g., “cat vs. not cat”). Generative AI learns patterns deeply enough to create new content (text, images, audio, video). Modern generative models rely on transformers and self-attention to capture long-range context, enabling coherent, context-aware outputs from short prompts.
Are generative AI outputs reliable? How can I validate and reduce bias?
- Reliability: Outputs can hallucinate. Mitigate by setting clear objectives, framing context, tuning LLM parameters, cross-validating, and adding robust validation steps.
- Bias: Limit knowledge scope, prefer models trained on diverse datasets, and conduct bias audits by testing with varied inputs.
- Also consider security and compliance to prevent misuse and protect user data.
Will developers lose jobs because of AI?
Routine tasks (e.g., code generation, documentation, testing) will be heavily automated, but developers who adopt AI can shift toward higher-value, creative, and system-level work. Like past technological shifts, those who upskill and leverage new tools remain in demand.
 Build AI-Enhanced Web Apps ebook for free
Build AI-Enhanced Web Apps ebook for free