1 Using generative AI in web apps
Generative AI web apps weave advanced models—especially large language models—into the browser experience to produce text, images, audio, and video on demand. This unlocks conversational interfaces, adaptive workflows, and personalized content that go beyond static logic. The chapter frames the book’s goal: help developers with basic JavaScript and React skills build production-grade AI features, integrating leading providers and patterns while staying focused on practical, real-world outcomes.
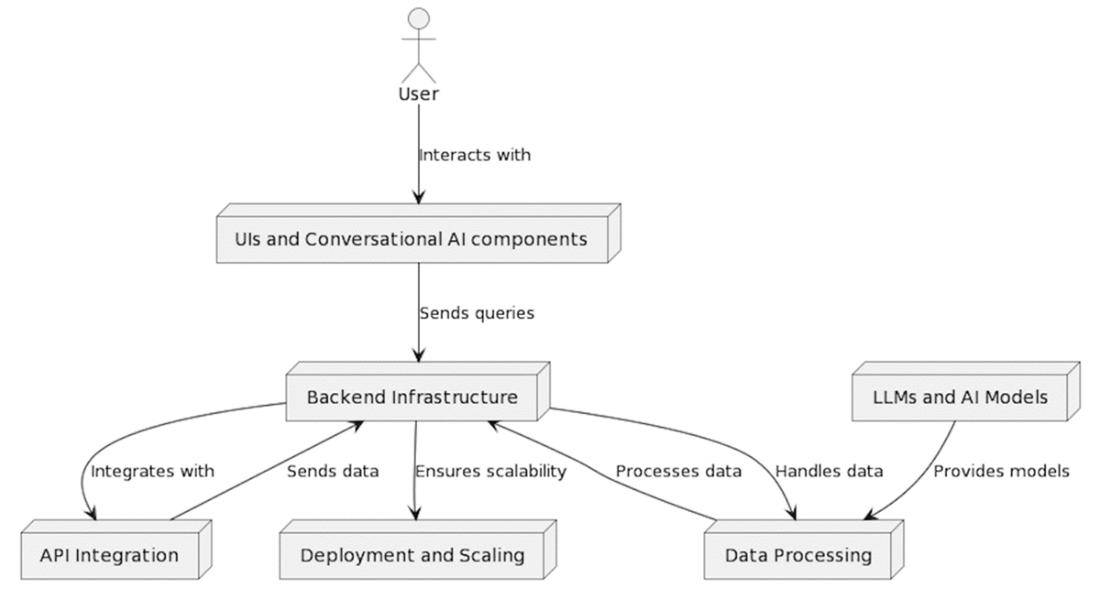
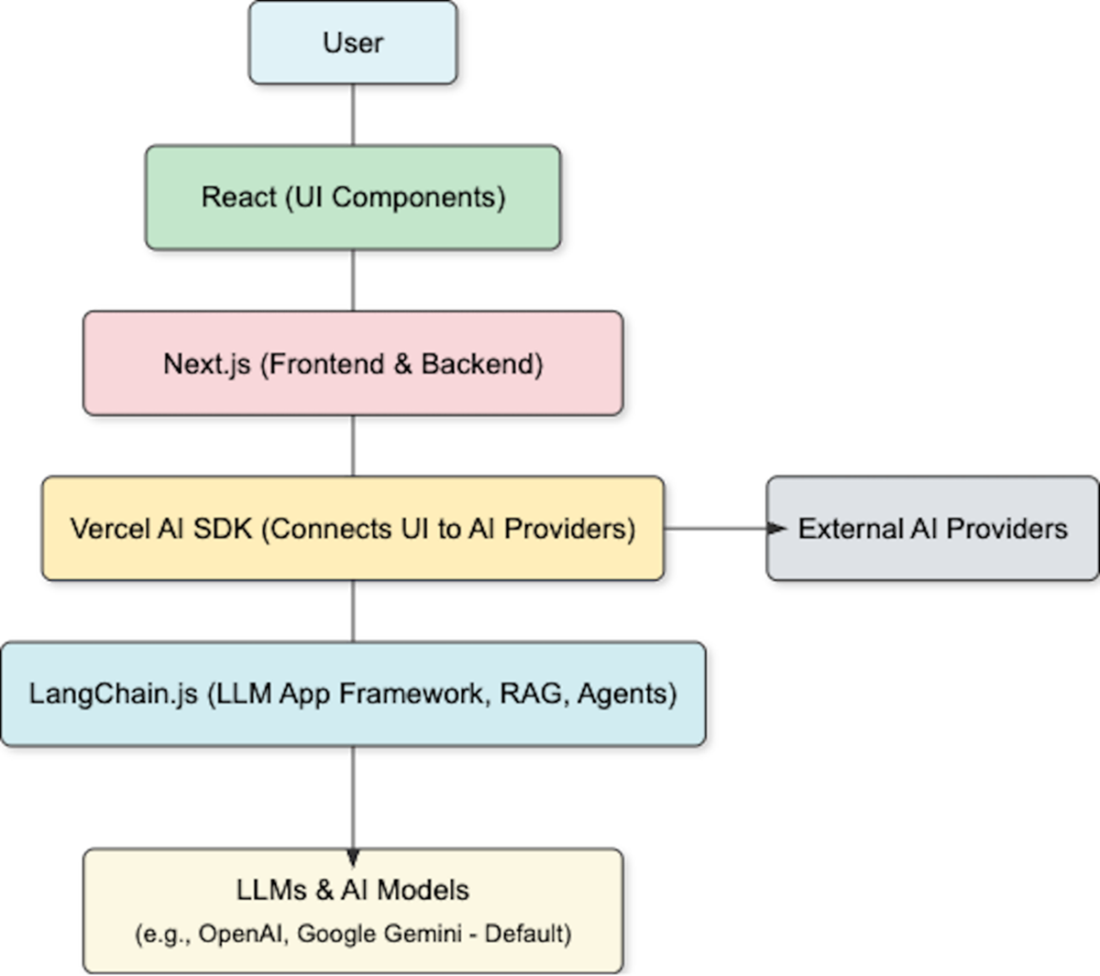
It explains how these apps operate end to end: users interact through UI components; backends clean and route inputs; the system selects models; content is generated and returned, often with a feedback loop. Core pieces include model access, conversational UIs, resilient backend infrastructure (caching, serverless, containers, and model serving), data pipelines, API integrations, and deployment for scale. The stack centers on React and Next.js with the Vercel AI SDK, plus LangChain.js for RAG and agentic patterns, and popular models like Gemini and OpenAI. The chapter also guides model selection—covering types such as transformers, GANs, and autoregressive models—alongside trade-offs between pre-trained services and self-hosting, and the performance considerations that shape UX.
Capabilities span text, image, multimedia, and code generation, with concrete use cases like marketing content toolboxes, customer support chatbots with dynamic responses, and mock interview agents with speech interfaces and adaptive coaching. The chapter balances enthusiasm with responsibility: it highlights quality control, security, cost, and regulatory compliance; techniques to validate outputs and reduce hallucinations; bias assessment and mitigation; and UX practices such as streaming and multimodal inputs to keep interactions fast and clear. It closes by noting the workforce impact of automation while emphasizing that developers who embrace these tools can focus on higher-level, creative work—and build reliable, user-centered AI applications.
The flow of information and interactions between the key components of a generative AI web application.
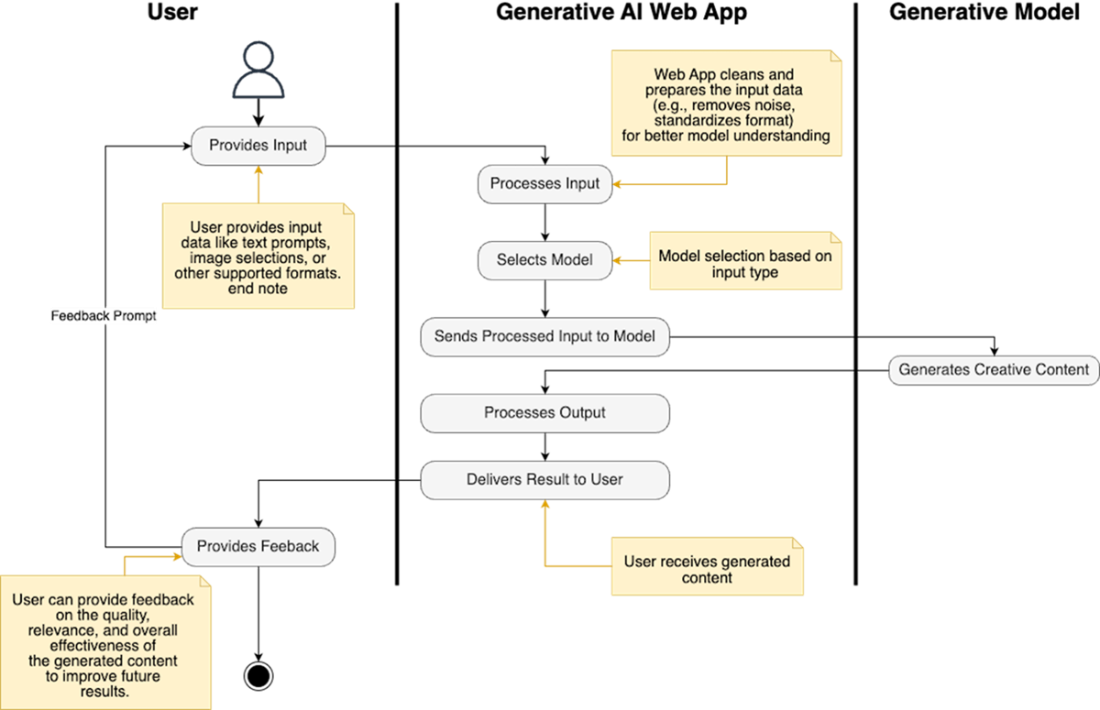
How an AI web app works: users input data, the app processes it, selects a model, generates content, delivers it, and optionally collects feedback.
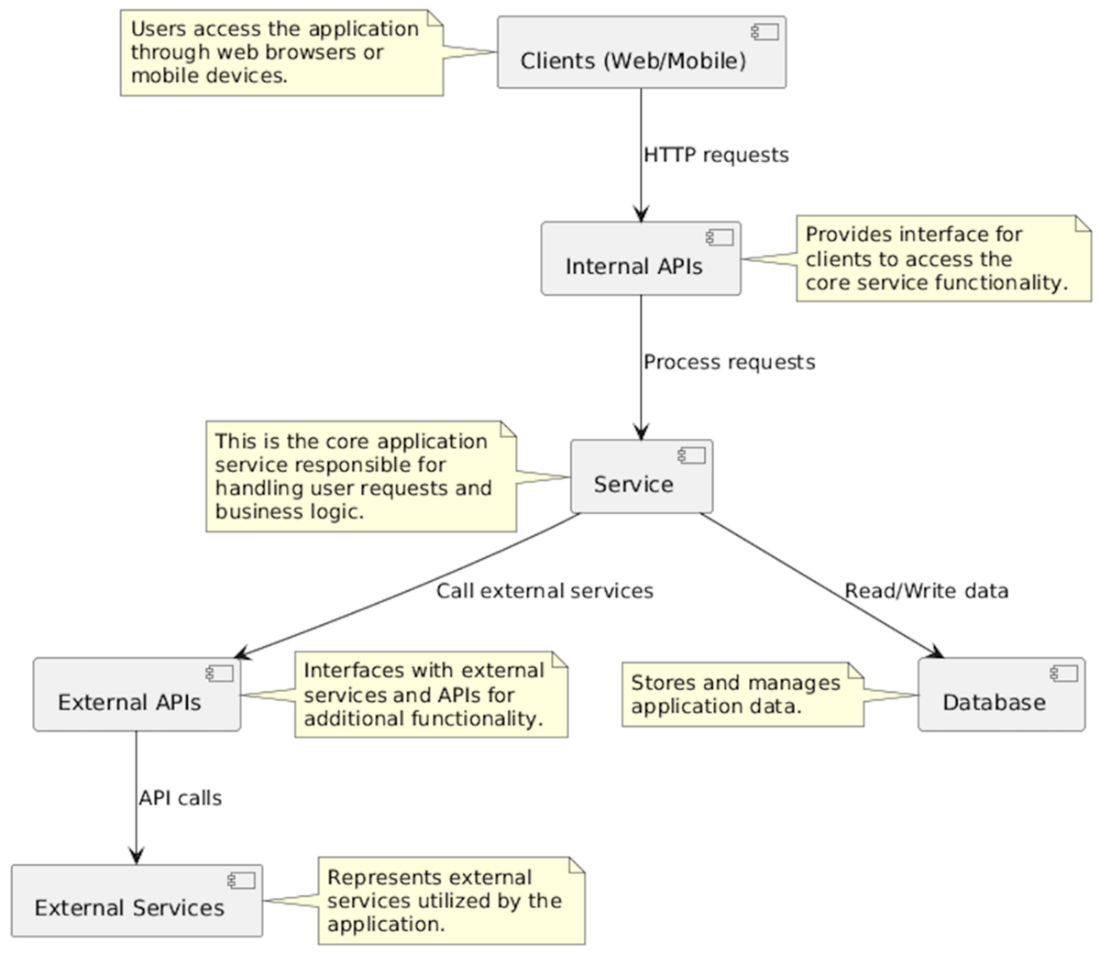
Simplified architecture diagram of a web application ecosystem. Clients, including web browsers and mobile devices, interact with the core application service, which handles user requests and business logic. The service interacts with a database to store and manage application data. Additionally, the service communicates with external APIs to access additional functionality and interacts with external services utilized by the application.
Leveraging key technologies to create generative AI web applications
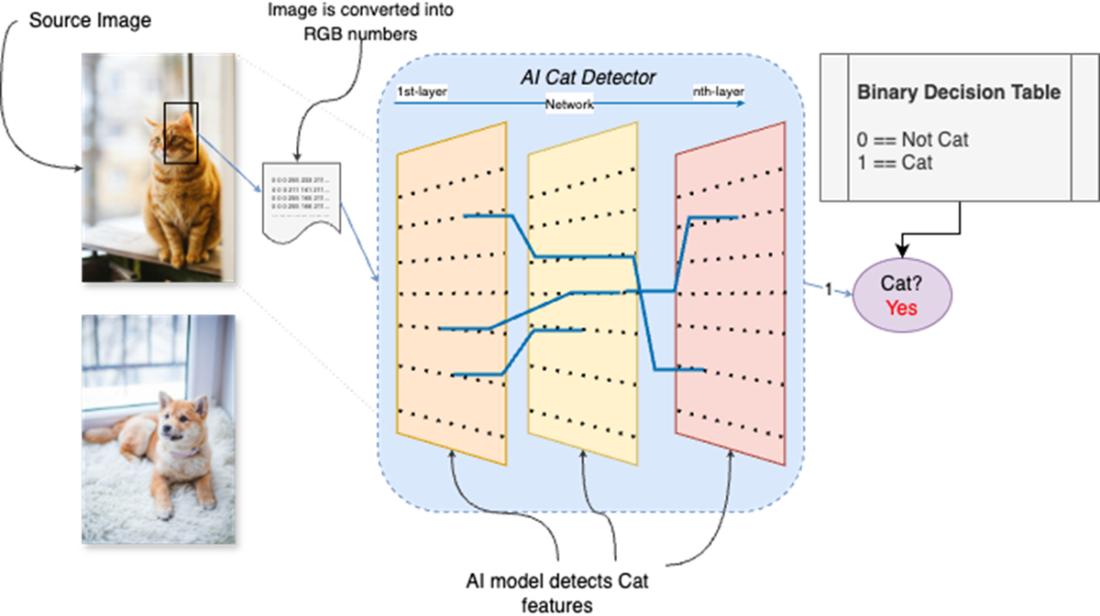
How AI can be used to detect whether a picture of a cat is a cat or not. It accepts an image as input and responds with yes or no (or 0 and 1).
Summary
- Generative AI can generate not only text, but all sorts of media resources like images, video clips and audio. This greatly enhances their potential usage in web applications, and real-world uses of generative AI in web applications range from digital marketing and customer experience management to mock interview applications.
- Generative AI web apps center on powerful models like large language models (LLMs) to create content from user input. The apps require a full supporting ecosystem to integrate with the model, including UI and conversational AI components, backend infrastructure, data processing pipelines, API integration, and deployment and scaling mechanisms.
- The apps we build in this book will use JavaScript and React to display the UI interface components, along with Next.js and the Vercel AI SDK to manage the backend and interact with external AI service providers.
- Choosing the right model for an app is a key architectural decision and depends on the task required. Different model types ( such as LLMs, GANs, autoregressive, transformers, VAE, and RNNs) excel at different kinds of problems. But the model architecture is just one consideration; developers also need to consider the quality and type of data it was trained on.
- Software engineers have been using AI long before generative AI came into existence. Common applications include machine learning, search recommendations, chatbots and computer vision.
- Foundational research like Google's "Attention is All You Need" laid the groundwork for transformative technologies such as transformers, which simplified natural language processing tasks by leveraging attention mechanisms. Transformers revolutionized language modeling by improving efficiency and accuracy in understanding textual data, addressing long-standing challenges faced by traditional AI models.
- Limitations of generative AI include quality control issues, resource intensiveness, security concerns, and regulatory compliance. Concerns include its potential impact on jobs, the reliability of outputs, handling bias, and enhancing the user experience.
 Build AI into Your Web Apps ebook for free
Build AI into Your Web Apps ebook for free