1 The World of Large Language Models
Language sits at the core of human connection, and modern Natural Language Processing has evolved from early rule-based efforts to deep learning systems that can recognize patterns at scale. That evolution enabled the rise of Large Language Models—probabilistic next-word predictors trained on vast corpora—which can write, summarize, translate, converse, and reason across broad topics. They surpass early voice assistants by sustaining rich, context-aware dialogue and are increasingly complemented by multimodal models that combine text with images or audio. Framing LLMs as foundational building blocks, the chapter positions the book as a practical guide to applying them in real-world settings rather than dwelling on mathematical formalism.
The chapter surveys a wide application surface: conversational agents, text and code generation, information retrieval, language understanding, recommendation, content editing, and agentic task execution. Building such applications entails careful orchestration—from defining the use case and acquiring suitable compute, to pretraining on massive datasets, then fine-tuning for domain-specific needs. Training leverages large-scale web data and specialized hardware (e.g., GPUs/TPUs), with iterative optimization of weights and biases to internalize linguistic patterns. Retrieval-Augmented Generation features prominently: it first fetches relevant context from a curated knowledge base and then conditions the model’s response on that evidence, improving specificity and freshness for focused domains.
Scale is both the superpower and the constraint: large models capture nuanced grammar and context yet demand significant compute and cost. The chapter underscores key challenges—data bias, ethical risks, limited interpretability, and hallucinations—arguing for guardrails, validation, and responsible deployment. It also maps the startup landscape catalyzed by LLMs, from lightweight wrappers to infrastructure platforms (vector databases and frameworks) and capital-intensive model labs competing at the frontier. Funding patterns mirror complexity and defensibility, with infrastructure and “GPU-rich” players attracting outsized investment. The chapter closes by setting expectations for the book’s focus: building effective LLM applications and exploring the components that make them reliable, practical, and impactful.
An output for a given prompt using ChatGPT
Rose Goldberg’s famous self-operation napkin constructing an LLM application demands a thoughtful orchestration of resources, from computational power to application definition, echoing the complexity of Rube Goldberg's contraptions.
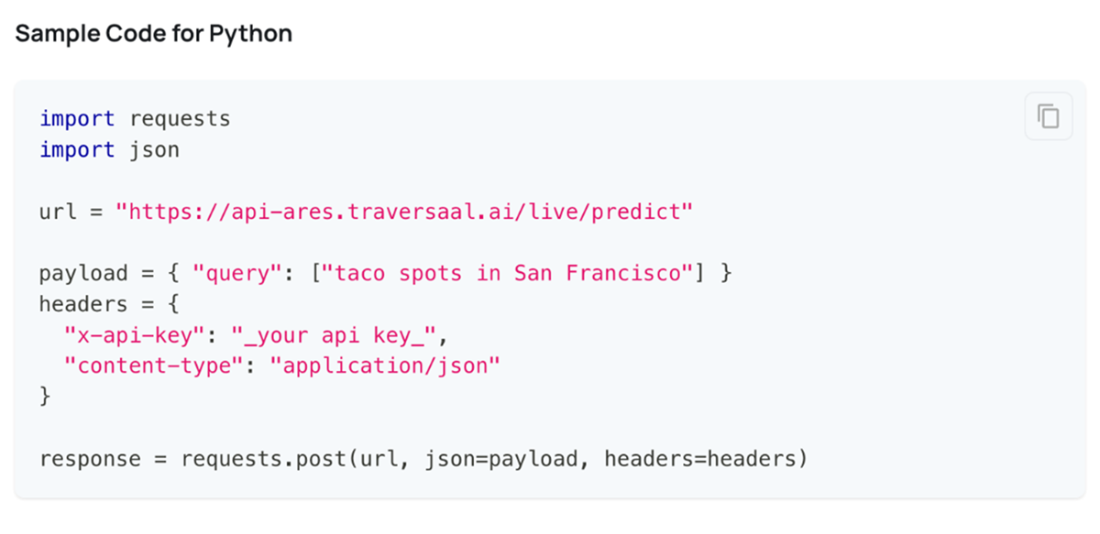
A Python code snippet demonstrating how to use the Ares API to retrieve information about taco spots in San Francisco using the internet. Instead of just showing URLs, the API returns actual answers with web URLs as source
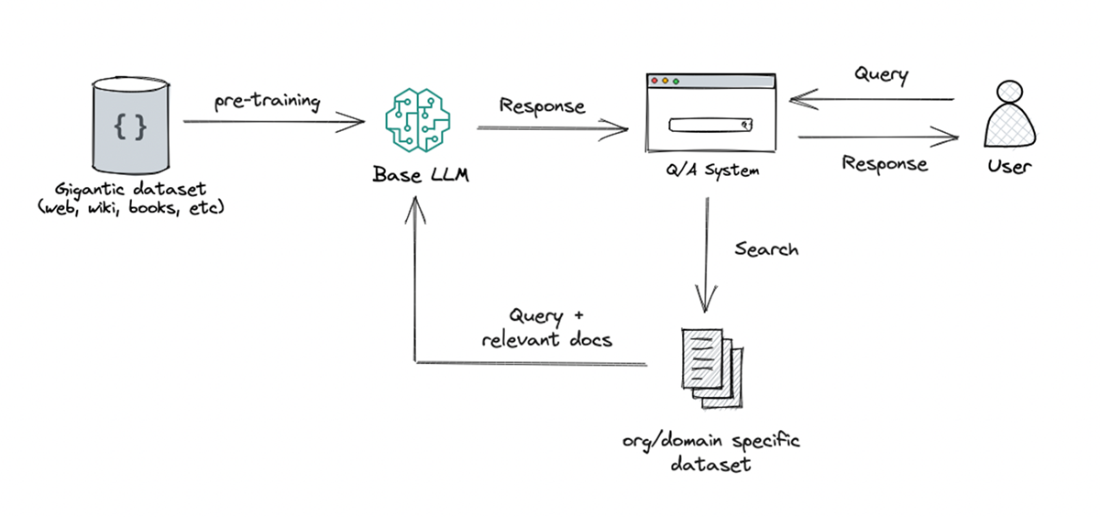
Retrieval Augmentation Generation is used to enhance the capabilities of LLMs, especially in generating relevant and contextually appropriate responses. The approach involves incorporating an initial retrieval step before generating a response to leverage information from a knowledge base.
Summary
- Large language models (LLMs) are the latest breakthrough in natural language processing after statistical models and deep learning. LLMs stand on the shoulders of this prior research but take language understanding to new heights through scale.
- Pretrained on massive text corpora, LLMs like GPT-3 capture broad knowledge about language in their model parameters. This allows them to achieve state-of-the-art performance on language tasks.
- Applications powered by LLMs include text generation, classification, translation, and semantic search to name a few.
- LLMs utilize multi-billion parameter Transformer architectures. Training such gigantic models requires massive computational resources only recently made possible through advances in AI hardware.
- Bias and safety are key challenges with large models. Extensive testing is required to prevent unintended model behavior across diverse demographics.
- Numerous startups are offering LLM model APIs, democratizing access and allowing innovation in the realm of Generative AI.
FAQ
What is a Large Language Model (LLM) in simple terms?
An LLM is an AI system trained on massive amounts of text to predict the next word in a sequence. By learning patterns, context, and nuances in language, it can generate coherent, human-like text, answer questions, summarize, translate, and converse.
How are LLMs different from early virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa?
Early assistants primarily followed predefined rules and handled narrow, scripted tasks. LLMs go beyond that by generating rich, context-aware language, sustaining multi-turn conversations, and adapting to varied topics with human-like fluency.
What are the main applications of LLMs?
Common applications include conversational assistants, text and code generation, information retrieval and search, language understanding (sentiment, intent, NER), recommendation systems, content creation/editing, and agent-based task fulfillment.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and when should I use it?
RAG enhances an LLM by retrieving relevant snippets from a selected corpus before generation, giving the model fresh, context-specific grounding. It’s especially useful for specialized domains or up-to-date information, though it relies on the quality of the underlying documents and doesn’t guarantee correctness.
How does RAG work at a high level?
It typically follows four steps: (1) Retrieval: search a curated knowledge base for relevant content; (2) Candidate selection: identify the most relevant passages; (3) Context integration: add those passages to the prompt; (4) Response generation: the LLM produces an answer using both its prior training and the retrieved context.
Why do LLMs need so much data, and what datasets are used?
Vast, diverse data helps models learn general language patterns, semantics, and contextual cues, improves robustness, and reduces overfitting. One widely used source is Common Crawl, a public web-scale corpus spanning hundreds of billions of pages collected over many years.
What’s the difference between training and fine-tuning an LLM?
Training (pretraining) teaches the model general language patterns on massive datasets by adjusting weights and biases to predict the next word. Fine-tuning adapts that pretrained model to a specific task or domain (e.g., legal or medical) using a smaller, targeted dataset for better task-specific performance.
What compute is required to train or tune LLMs?
Training LLMs is compute-intensive, typically requiring distributed clusters of GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA data center GPUs) or TPUs. Depending on model size and resources, training can take weeks or months; fine-tuning is faster but still resource-demanding.
What limitations should I watch for (bias, ethics, interpretability, hallucinations)?
LLMs may reflect biases in their training data, produce misleading or harmful content, and are often hard to interpret. They can also “hallucinate”—confidently generating incorrect or nonsensical information—so validation and guardrails are essential.
What are the core components of an LLM application?
Typical components include: defining the use case; choosing or accessing the base model; data pipelines and retrieval (e.g., RAG with a vector database); prompt and context orchestration; training/fine-tuning where needed; serving infrastructure (GPUs/TPUs); and monitoring, evaluation, and safety controls.
 Build an LLM Application (from Scratch) ebook for free
Build an LLM Application (from Scratch) ebook for free