1 Introduction to Generative AI
This chapter introduces how generative AI augments, rather than replaces, software developers by supplying context-aware help across the coding lifecycle. Aimed primarily at Python programmers but applicable beyond, it shows how AI assistants accelerate implementation, improve test coverage and documentation, and elevate focus from boilerplate to design and architecture. It also maps the growing tool landscape—integrated IDE assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, Blackbox) and standalone chat tools (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot Chat)—and sets pragmatic expectations for productivity gains without requiring AI expertise.
The chapter explains the fundamentals behind large language models: transformer architectures, attention mechanisms, and probability-driven text and code generation refined through developer feedback. It contrasts generative AI with traditional code completion, emphasizing nondeterminism and the potential for “hallucinations,” and clarifies why LLMs differ from databases that retrieve fixed answers. It highlights training-data quality, bias, and context-interpretation issues, then offers mitigation strategies—provide precise requirements, relevant code context, constraints, and clear I/O contracts—to steer models toward accurate, maintainable results.
Practically, the chapter outlines an AI-augmented workflow from ideation and planning through scaffolding, coding, review, testing, debugging, and documentation, showing where integrated and standalone tools fit best. It offers criteria for choosing tools—data provenance and licensing, workflow and security integration, quality assurance, team adoption, and the pace of change—and argues that AI is a force multiplier that shifts effort toward problem solving, architecture, and ethics. Finally, it previews skills the book will build—context management, prompt engineering, testing integration, and architectural guidance—to help you ship faster with higher quality and confidence.
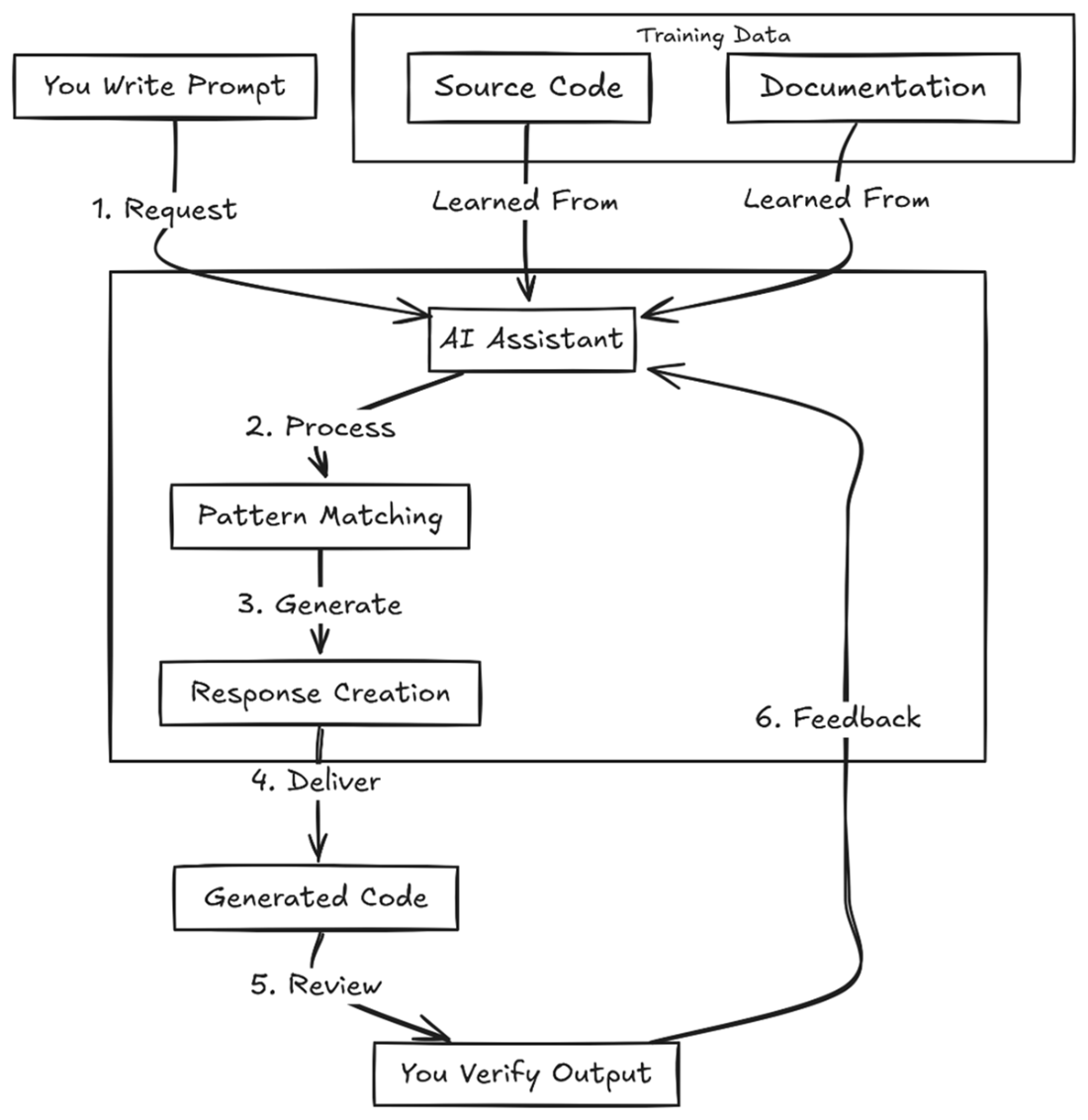
Integrated tools use a sophisticated system to generate code. It starts with your prompt, and the assistant gathers up documentation, and source code to see if your answer can come from these sources. It makes a best guess at what you’re looking for and generates a response. Your acceptance of these responses helps train the assistant in the future (unless you’ve blocked feedback).
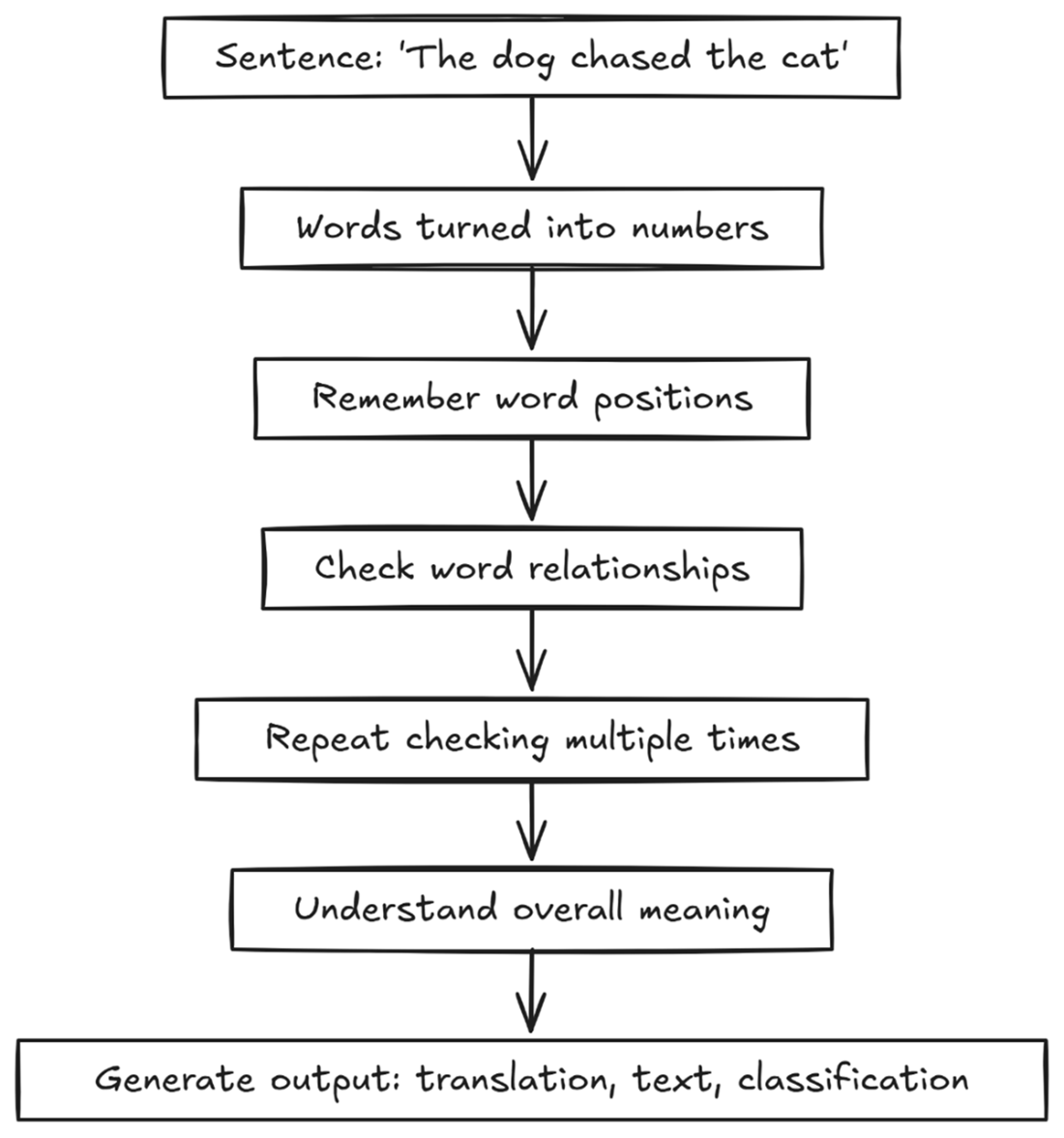
A transformer takes a sentence and analyzes word positions and relationships to try and extract meaning from the text it sees.
Mona Lisa riding a skateboard in the desert, courtesy of Midjourney

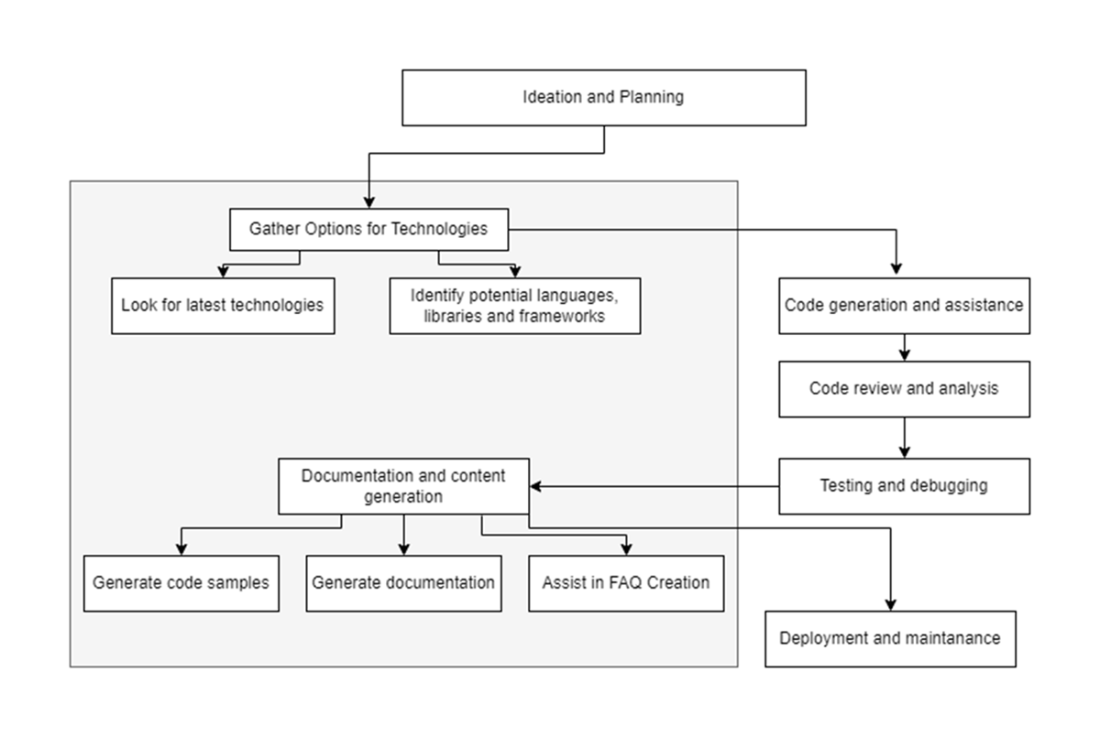
Generative AI tools play a big role in the planning process. From ideation and planning, to choosing a technology, to building the software and deploying it. Each of these steps can be enhanced with AI tooling.
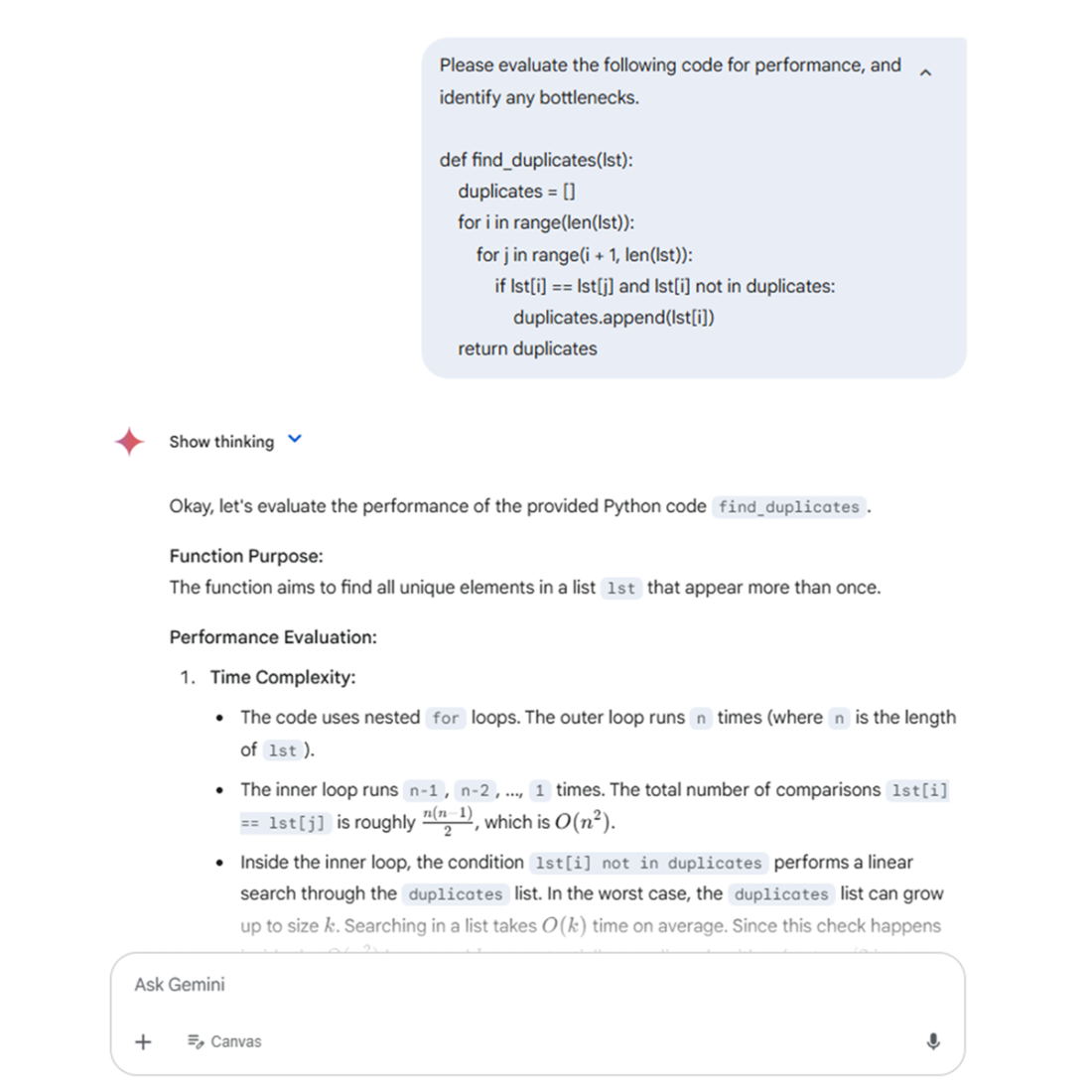
Even with a few lines of code Gemini can analyze it and make suggestions to improve it.
Summary
- Generative AI tools are changing software development. They boost productivity by generating code, finding bugs, and automating documentation.
- Modern AI tools come in two types: integrated tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine, which work in your IDE, and standalone solutions like ChatGPT and Gemini for bigger tasks.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) drive these tools. They learn patterns from huge code datasets, helping them create relevant code based on probabilities.
- It's important to know that AI tools make predictions, not certain outcomes. This understanding sets realistic expectations and shows why checking results is key.
- The AI-assisted development workflow includes ideation, planning, coding, testing, and documentation. Each phase gains unique benefits from AI support.
- To adopt AI tools effectively, consider training data quality, how they fit into workflows, quality assurance processes, and the need to adapt to new tools quickly.
- AI tools do not replace developers. Instead, they take care of routine tasks, letting humans focus on problem-solving, design, and creativity.
- As you read this book, you’ll discover ways to use these tools, making them valuable partners in your Python development process.
 Coding with AI ebook for free
Coding with AI ebook for free