1 Why authorization matters: Securing access in a digital world
Authorization determines what actions principals can take on which resources, and this chapter explains why it is as fundamental as authentication in a world of cloud, multi-tenant, and interconnected systems. Using incidents like the 2013 Target breach as cautionary context, it shows how weak authorization boundaries, vendor access, and slow response can turn a minor compromise into a major disaster. Beyond security, authorization also enables core product capabilities—from document sharing in collaborative apps to scalable, customer-controlled access in cloud platforms—making it indispensable to modern digital experiences.
The chapter grounds authorization in digital identity’s purpose: systems must recognize, remember, and relate to entities across distance and at scale. Traditional static methods such as file permissions, ACLs, and RBAC struggle with today’s realities—combinatorial growth, dynamic context (time, device, location), transient roles, cross-organization collaboration, and stringent audit and compliance demands. These limitations lead to over-permissioning, opaque decisions, and inconsistent enforcement, and they are especially incompatible with zero trust models that authorize every request. Dynamic authorization addresses these gaps by decoupling access logic from application code and evaluating fine-grained, context-aware policies at runtime, using complementary approaches: Policy as Code for reusable, testable rules and Policy as Data for rich, per-resource relationships.
Adopting dynamic, policy-driven authorization delivers concrete business value. It reduces operational cost and risk by automating access decisions, shrinking permissions sprawl, streamlining onboarding/offboarding, and improving auditability. It boosts agility and customer experience by enabling granular sharing, delegated administration, subscription and feature gating, and partner access without bespoke code. And it strengthens security and compliance across SaaS, zero trust, IoT, and AI-driven use cases through least-privilege, context-sensitive control and verifiable logs. The chapter concludes that dynamic authorization is a strategic imperative—an engine for efficiency, resilience, and competitive differentiation in a highly regulated, rapidly evolving digital landscape.
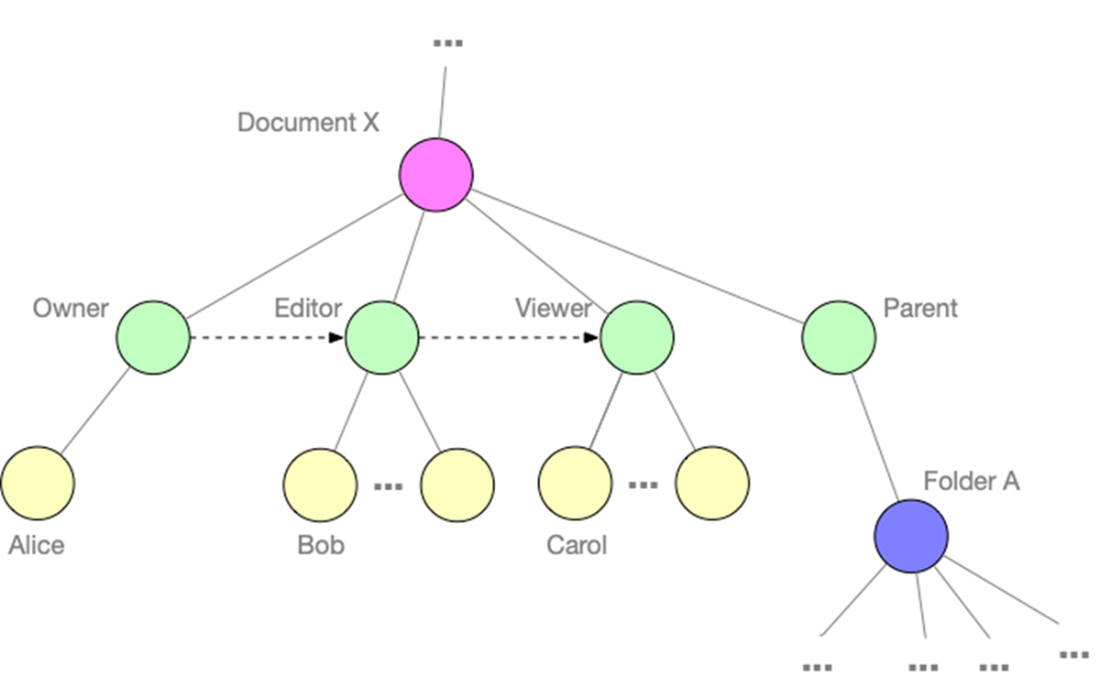
A relationship graph representing access to a Google document. Rather than use static ACLs, this model captures roles (like Owner, Editor, Viewer) as first-class relationships between users and resources. The graph also models hierarchical relationships (such as parent folders), enabling more flexible, general-purpose authorization logic that can be queried and evaluated dynamically.
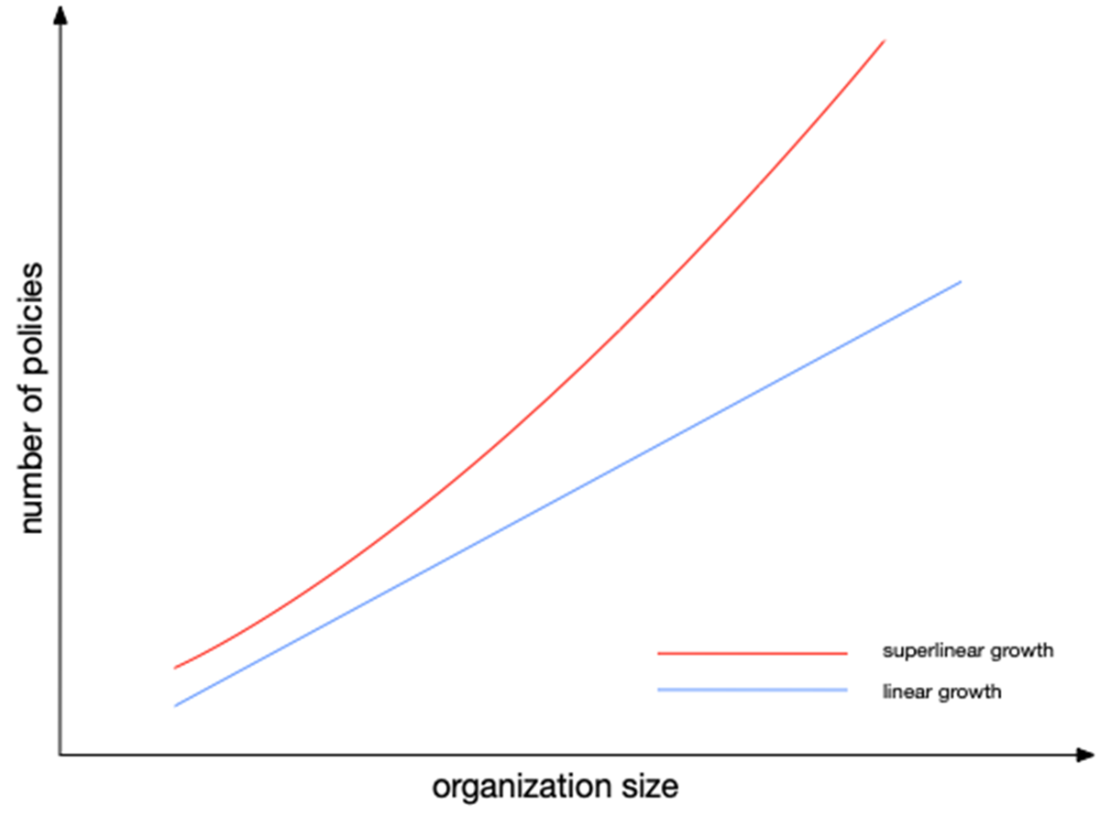
As an organization grows, the number of access policies tends to increase faster than linearly. Though a small organization might manage with a simple, flat set of policies, larger organizations face compounding complexity due to team structures, regional compliance, and overlapping responsibilities, leading to superlinear policy growth.
Summary
- Poor access control can lead to severe security breaches, as seen in the Target breach, where attackers exploited weak authorization to access sensitive systems.
- Authorization is not just about security; it also enables key features in modern cloud applications, such as document sharing and multi-tenant access control.
- Traditional authorization methods like ACLs and RBAC are static and struggle with scalability, flexibility, maintainability, efficiency, auditability, and security.
- Dynamic authorization overcomes these challenges by using policies to make real-time, context-aware access decisions.
- Policy-based access control (PBAC) enables fine-grained authorization by externalizing access control logic, making it dynamic and adaptable to changing conditions.
- The shift toward zero-trust security models, SaaS applications, IoT, regulatory compliance, and AI-driven applications demands more flexible and scalable access control, making dynamic authorization essential.
- Policies can be represented as code or data, enabling both structured rule enforcement and flexible, real-time access adjustments.
- Treating policy as code allows version control, testing, and automation, while policy as data supports fine-grained, user-defined access controls.
- Organizations adopting dynamic authorization benefit from reduced operational costs, improved agility, enhanced security, and better customer experiences.
- Businesses can use dynamic authorization as a competitive advantage, enabling new product capabilities, faster compliance adaptation, and stronger security.
- Authorization is a strategic investment, not just a security measure—organizations that adopt policy-based access control gain efficiency, scalability, and security.
 Dynamic Authorization ebook for free
Dynamic Authorization ebook for free