1 Intro to enterprise RAG
Imagine a tireless digital assistant that understands natural questions, finds the right data instantly, and writes clear answers. That is the promise of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): it fuses a language model’s conversational ability with targeted retrieval from company sources like databases, documents, and internal apps. The chapter introduces RAG at a high level, explains how it works end to end, and contrasts simple “naive” setups with the enterprise-grade approach needed for real-world complexity. It frames the core goal as fast, accurate, and trustworthy access to knowledge so teams can make better decisions with less friction.
The text details why naive RAG struggles in business settings—returning irrelevant context, hallucinating, and failing at scale—and defines Enterprise RAG as a robust pipeline designed for reliability. Key capabilities include input validation, question triage, query rewriting, asynchronous agent orchestration, and hybrid enterprise search that blends keyword and vector retrieval. Results are ranked and filtered before a writer agent produces consistent, grounded answers. Beyond speed and accuracy, the chapter emphasizes multilingual support, up-to-date data, guardrails for safety, privacy controls, cost management, and observability. Practical benefits span faster customer support, smoother collaboration, and better decision-making, illustrated across small business, large enterprise, healthcare, finance, and education scenarios.
Finally, the chapter previews how to build such a system: start with evaluation, then ingest both unstructured and structured data; chunk documents thoughtfully, attach metadata, and generate embeddings for vector search. On retrieval, rewrite messy user questions into precise queries and combine multiple searches to gather the best evidence. For generation, assemble concise, user-friendly answers grounded in retrieved context with traceability. The result is a scalable, adaptable Enterprise RAG that turns scattered information into an accessible, trusted asset—and a practical roadmap for readers to implement it in their own organizations.
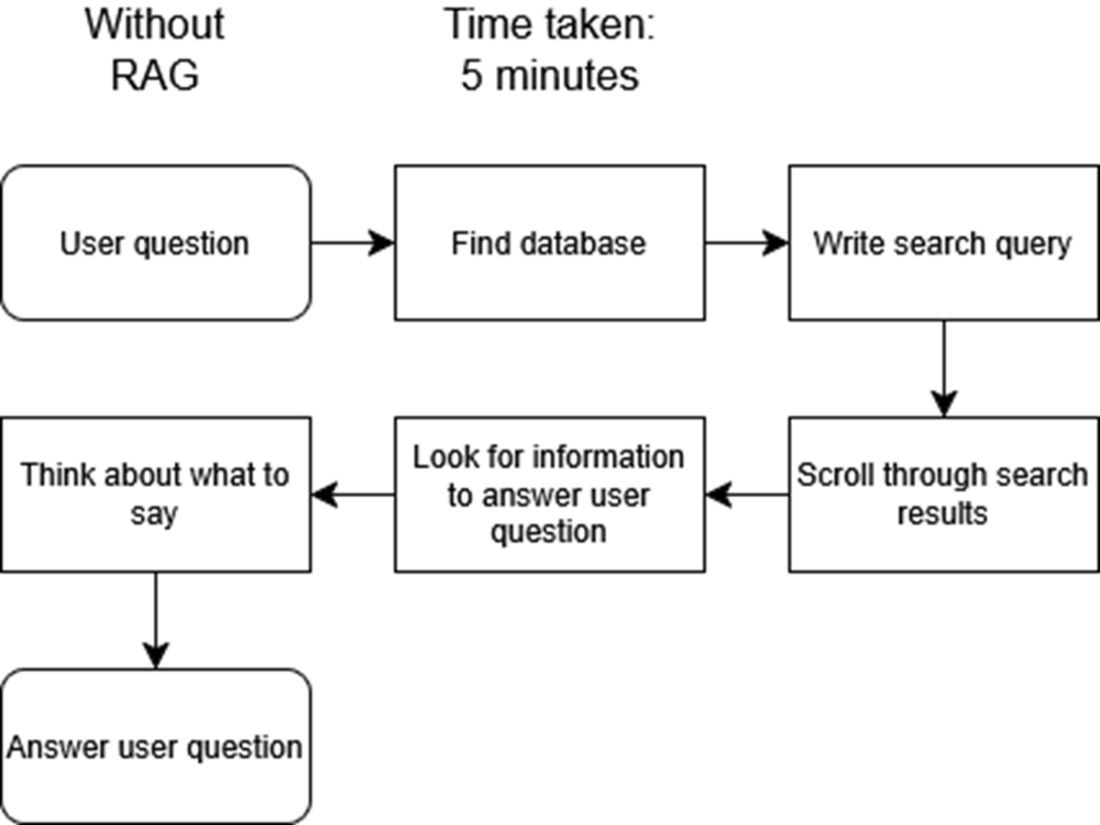
The left column shows the multiple steps and complexity of manually searching a SQL database for records. Compare this with the relative ease and simplicity of asking the question of a RAG chatbot instead,shown in the right column.

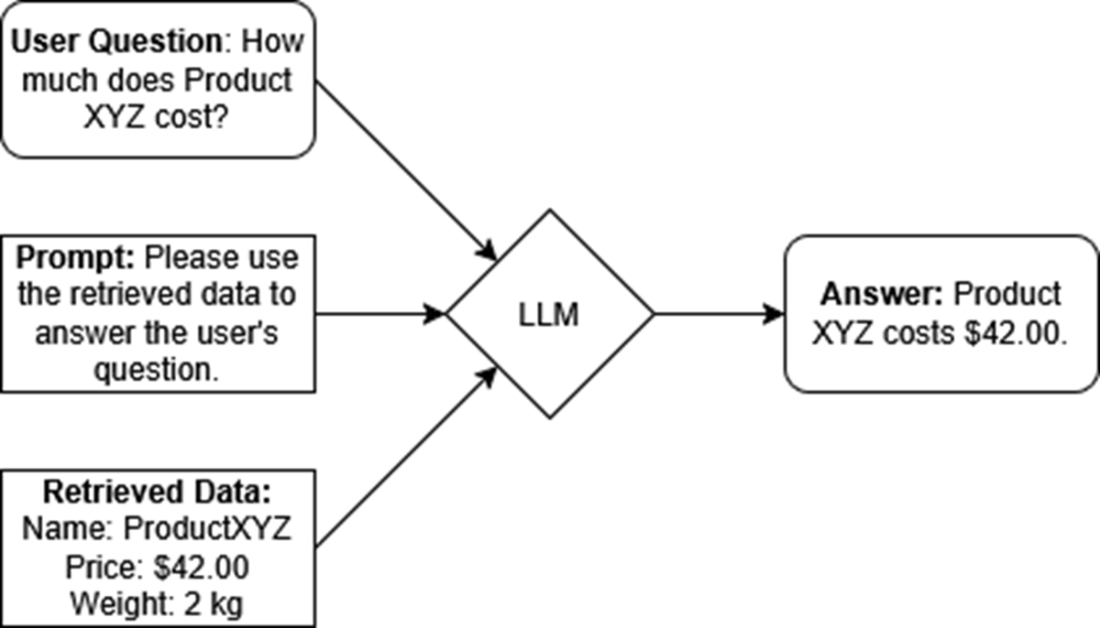
In a RAG system, the user question, the prompt, and the retrieved data are combined and sent to an LLM, which generates an answer using all that input information.
Traditional manual workflow for retrieving answers, requiring database queries, corrections, and manual review. This process is time-consuming, and requires a lot of effort.
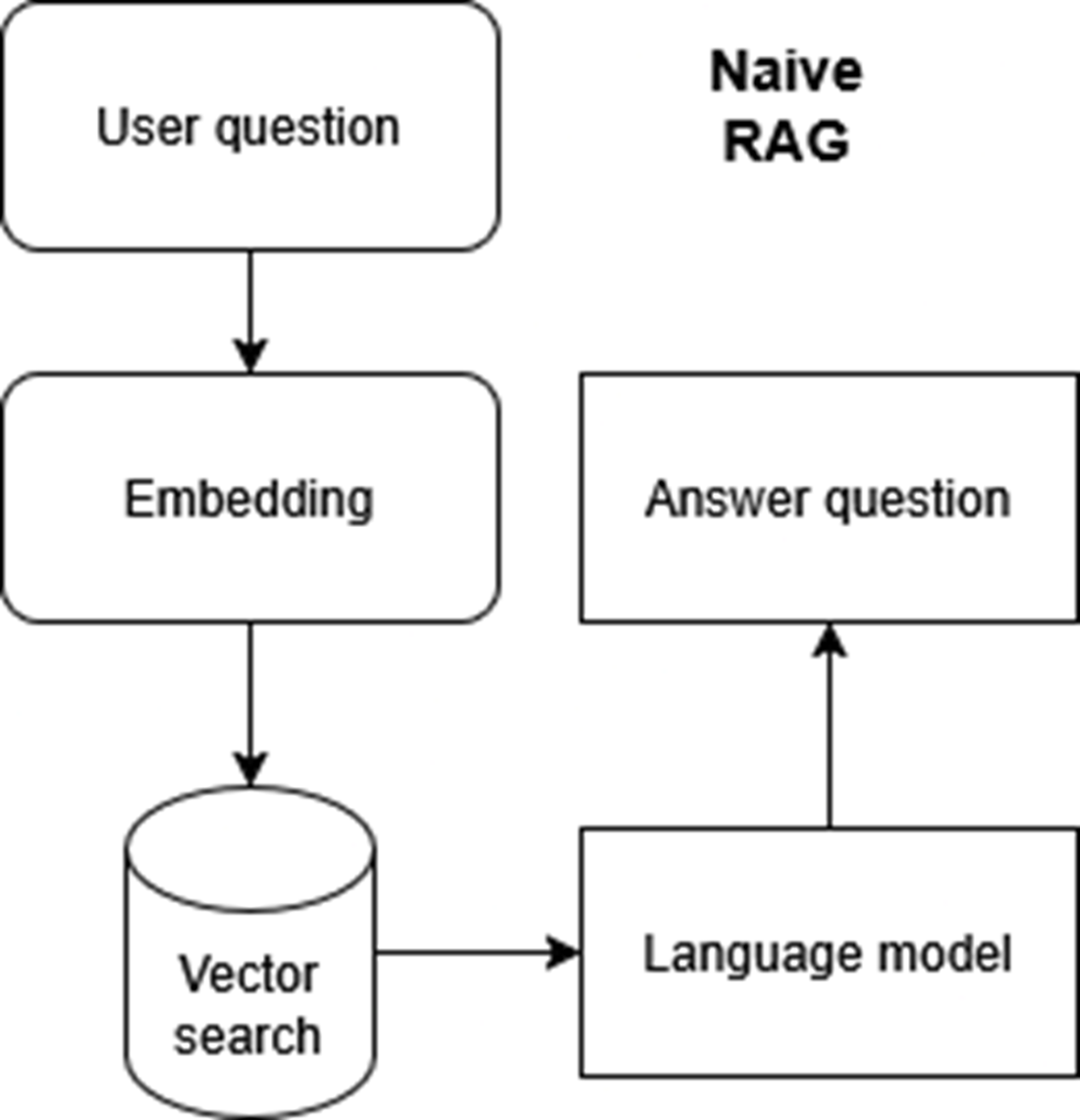
Basic RAG process with embedding, vector search, and a large language model. This simple approach is efficient but prone to errors and lacks context handling.
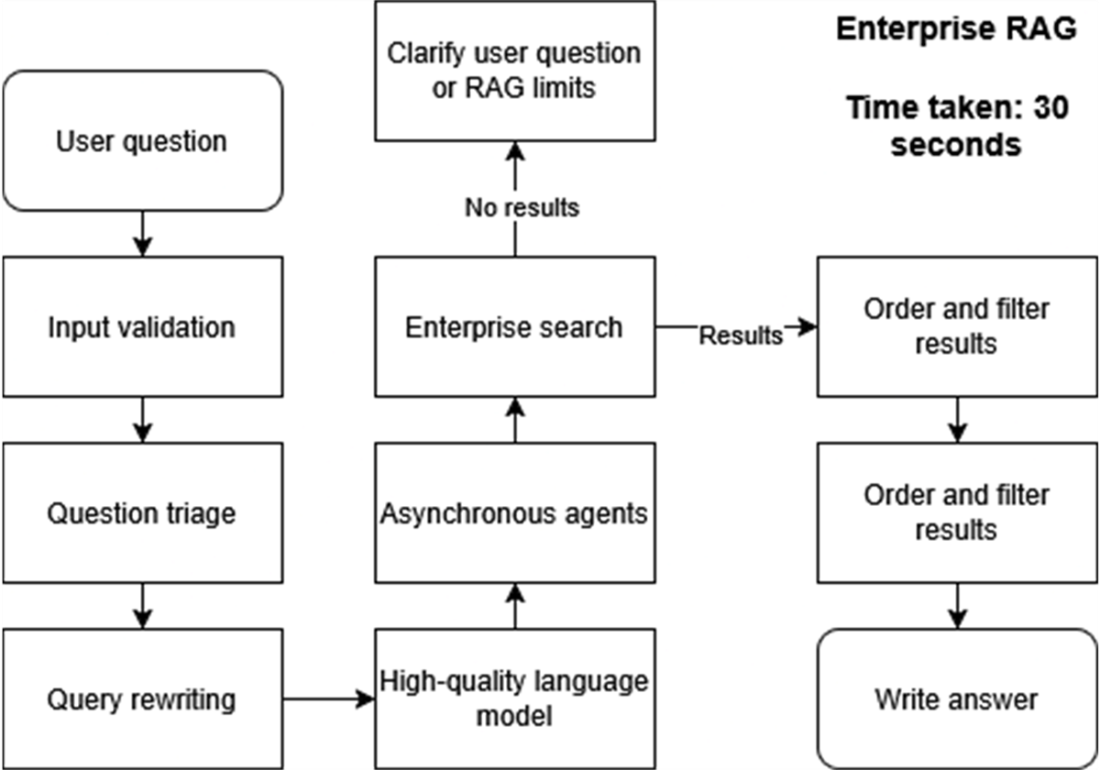
Enterprise RAG pipeline improves speed, accuracy, and scalability by incorporating validation, query rewriting, and asynchronous agents, reducing response times to 30 seconds..
A naive RAG pipeline with limited steps for retrieving answers. Suitable for simple queries but insufficient for handling complex or large-scale enterprise needs.
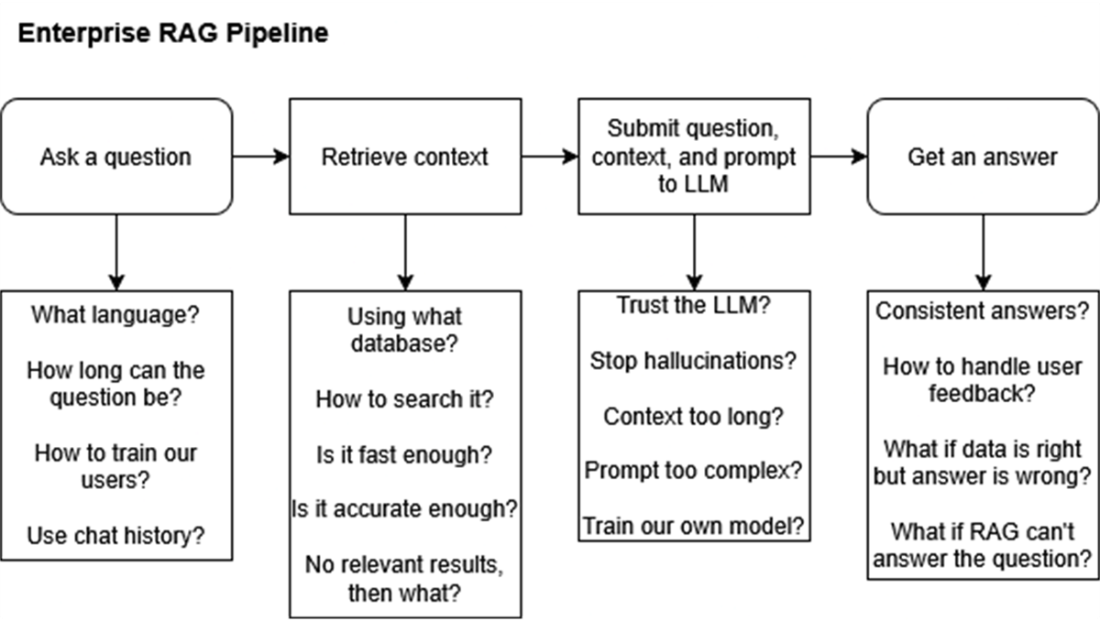
Key questions for designing enterprise RAG systems, addressing user input limits, database performance, context accuracy, and feedback management for better scalability and reliability.
Enterprise RAG system architecture showing ingestion, retrieval, and generation steps. Raw data is preprocessed, embedded, and searched to deliver accurate, context-aware answers.
Summary
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is an advanced AI technology that combines conversational skills with real-time data retrieval, like an efficient assistant.
- RAG allows users to ask questions in plain language and receive detailed, specific information tailored to their needs, accessing data from databases, documents, and applications like Slack.
- Naive RAG, while easy to set up, often falls short in business environments due to misunderstandings of context, retrieving incorrect data, or providing inaccurate ("hallucinated") answers.
- Enterprise RAG is designed to handle complex business scenarios, accurately processing diverse questions in different languages and grasping user intent.
- Implementing Enterprise RAG leads to streamlined operations, faster decision-making, improved collaboration, and enhanced customer service by resolving issues quickly.
- The book will guide readers step-by-step in building their own Enterprise RAG system, empowering them to harness the full potential of AI-driven data retrieval.
FAQ
What is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG is an AI approach that combines a language model’s conversational abilities with real-time retrieval from your data sources. You ask a question in plain language, the system searches relevant databases and documents, and the language model generates a clear, context-aware answer using the retrieved information.How is RAG different from a traditional database search?
Traditional search requires knowing where to look, crafting exact queries, and manually reviewing results. RAG lets you ask natural questions; it finds the right sources (across databases, files, apps), retrieves the most relevant snippets, and writes a coherent answer, dramatically reducing steps and effort.What is “Naive RAG,” and how does it work?
Naive RAG typically turns the user question into an embedding, searches a vector database for semantically similar chunks, and feeds the top matches plus the question to a language model to draft an answer. It’s simple and works for basic queries but struggles with scale and complexity.Why does Naive RAG often fail in business settings?
Common issues include retrieving the wrong context, mixing unrelated content, and hallucinations—especially with large, messy, or multi-source datasets. In complex, enterprise scenarios, this leads to inaccurate answers and poor reliability; estimates suggest many early business RAG attempts fail due to these pitfalls.What is “Enterprise RAG,” and what makes it different?
Enterprise RAG is a robust pipeline designed for real-world business needs. It adds steps such as input validation, question triage, query rewriting, asynchronous agents, multi-source enterprise search (keyword + vector), ordering and filtering results, and a writer agent. The result is higher accuracy, faster performance, and better scalability and usability.How does Enterprise RAG reduce errors and hallucinations?
It validates inputs, routes questions to the right paths, rewrites queries to match data schemas, searches across sources with combined methods, filters irrelevant results, and has a writer agent compose grounded answers. It also prompts for clarification when needed and applies guardrails to avoid unsafe or misleading outputs.What kinds of data sources can Enterprise RAG use?
Enterprise RAG connects to structured and unstructured data: SQL/operational databases, PDFs and documents, internal communications (e.g., Slack), and other business apps and indexes. It’s designed to search across many systems simultaneously and keep results current.What benefits can a business expect from Enterprise RAG?
- Faster decisions and responses (e.g., cutting a five-minute lookup to ~30 seconds in examples)- Higher accuracy and consistency across queries
- Productivity gains and better collaboration
- Improved customer support (e.g., notable reductions in time-per-issue in practice)
What risks and considerations should we plan for?
- Cost and operations: model usage, search services, and compute can add up; monitor and optimize workflows- Skills and maintenance: requires AI/ML/data engineering expertise and ongoing updates
- Safety and compliance: apply guardrails, control access, prevent data leaks, and handle legal risks from incorrect answers
- Multilingual and ambiguous queries: ensure triage and rewriting for reliability across languages and styles
 Enterprise RAG ebook for free
Enterprise RAG ebook for free