1 Intuition of AI
Artificial intelligence has moved from a niche research topic to a core capability in modern software engineering. This chapter sets the stage by building intuition for how AI systems work, focusing less on buzzwords and more on the mechanics behind them. It frames AI as autonomous, adaptive systems fueled by data, and outlines the journey the book will take—from classic search and evolutionary techniques through machine learning and deep learning, to today’s generative models—so readers can reason about, implement, and innovate with AI in practice.
The chapter clarifies key foundations: what counts as AI (systems performing tasks associated with human intelligence), why data quality and representation matter (quantitative vs. qualitative data, and the pipeline from data to information to knowledge), and how algorithms function as recipes that transform inputs into outputs. It distinguishes algorithms from models (the solver vs. the artifact), contrasts deterministic with probabilistic behavior, and introduces a practical taxonomy of problem types—search, optimization, prediction, classification, and clustering. It also places today’s systems in context: the evolution of techniques across decades; the spectrum from narrow intelligence to aspirational general and super intelligence; and the complementary roles of “old AI” (explicit logic and search) and “new AI” (learning from data).
Finally, it surveys the main families of algorithms the book explores and where they shine in the real world. Search algorithms underpin planning and pathfinding; biology-inspired approaches like evolutionary methods and swarm intelligence tackle hard optimization; machine learning learns patterns via supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning; deep learning with neural networks enables perception and broader generalization; and generative models create new text, code, and images (e.g., transformers and diffusion). Concrete applications span agriculture optimization, fraud and anomaly detection in banking, NLP-powered email security, medical imaging diagnostics, logistics routing and packing, personalized fitness from wearable data, and game-playing agents trained via reinforcement learning—setting up the next chapters to move from definitions to implementation.
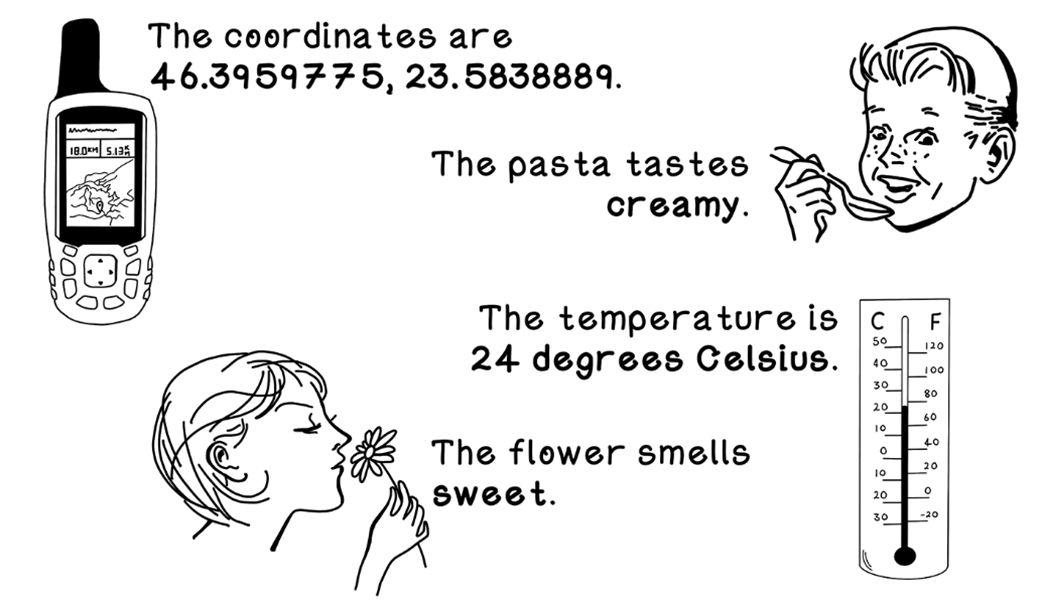
Examples of data around us
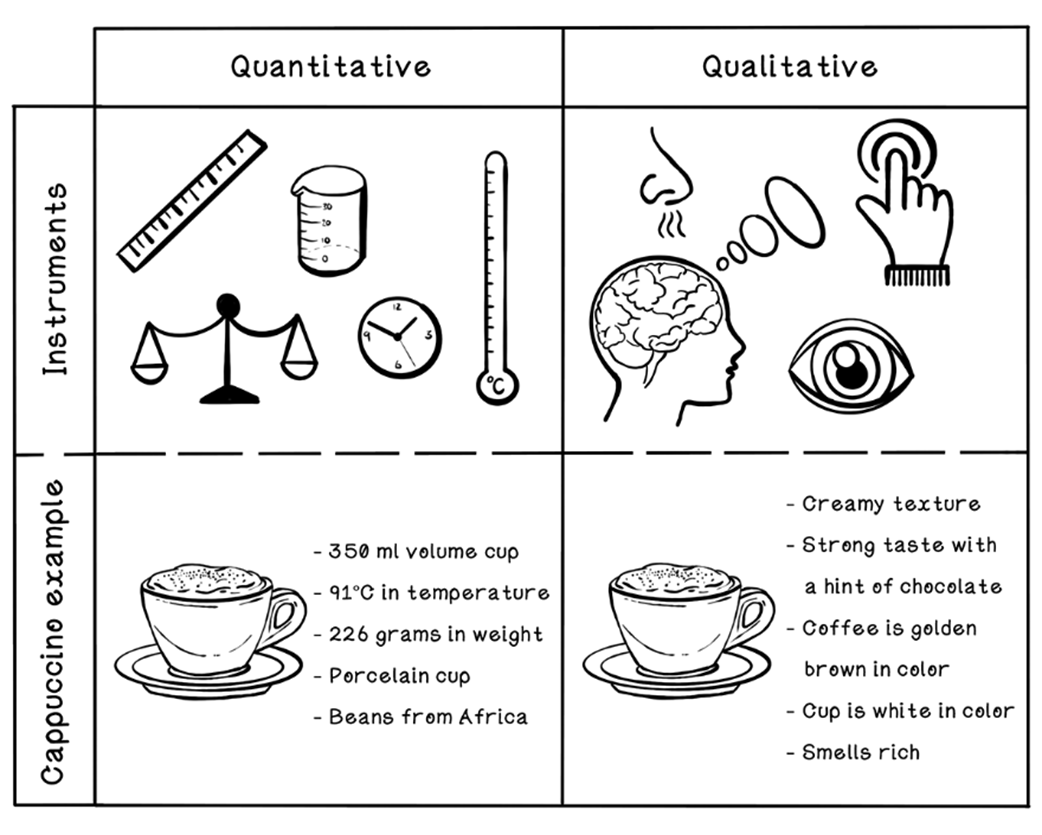
Qualitative data versus quantitative data
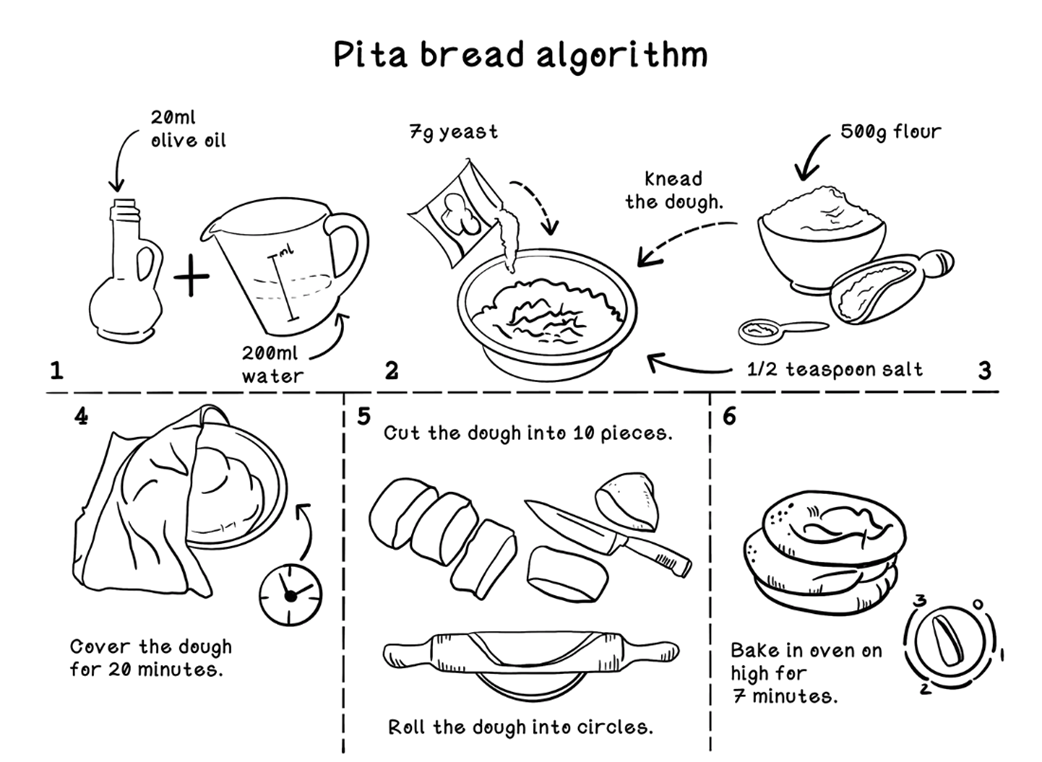
An example showing that an algorithm is like a recipe
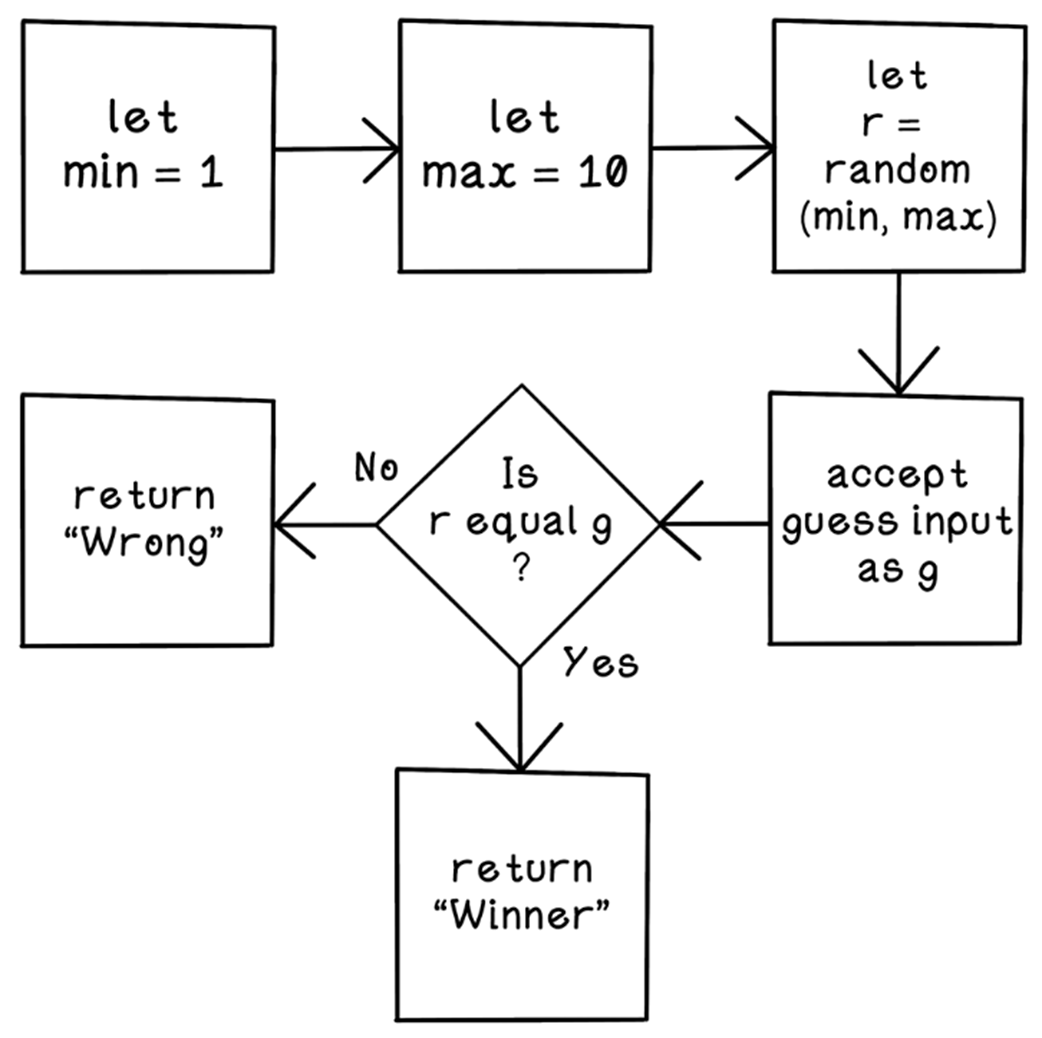
A number-guessing-game algorithm flow chart
The evolution of AI
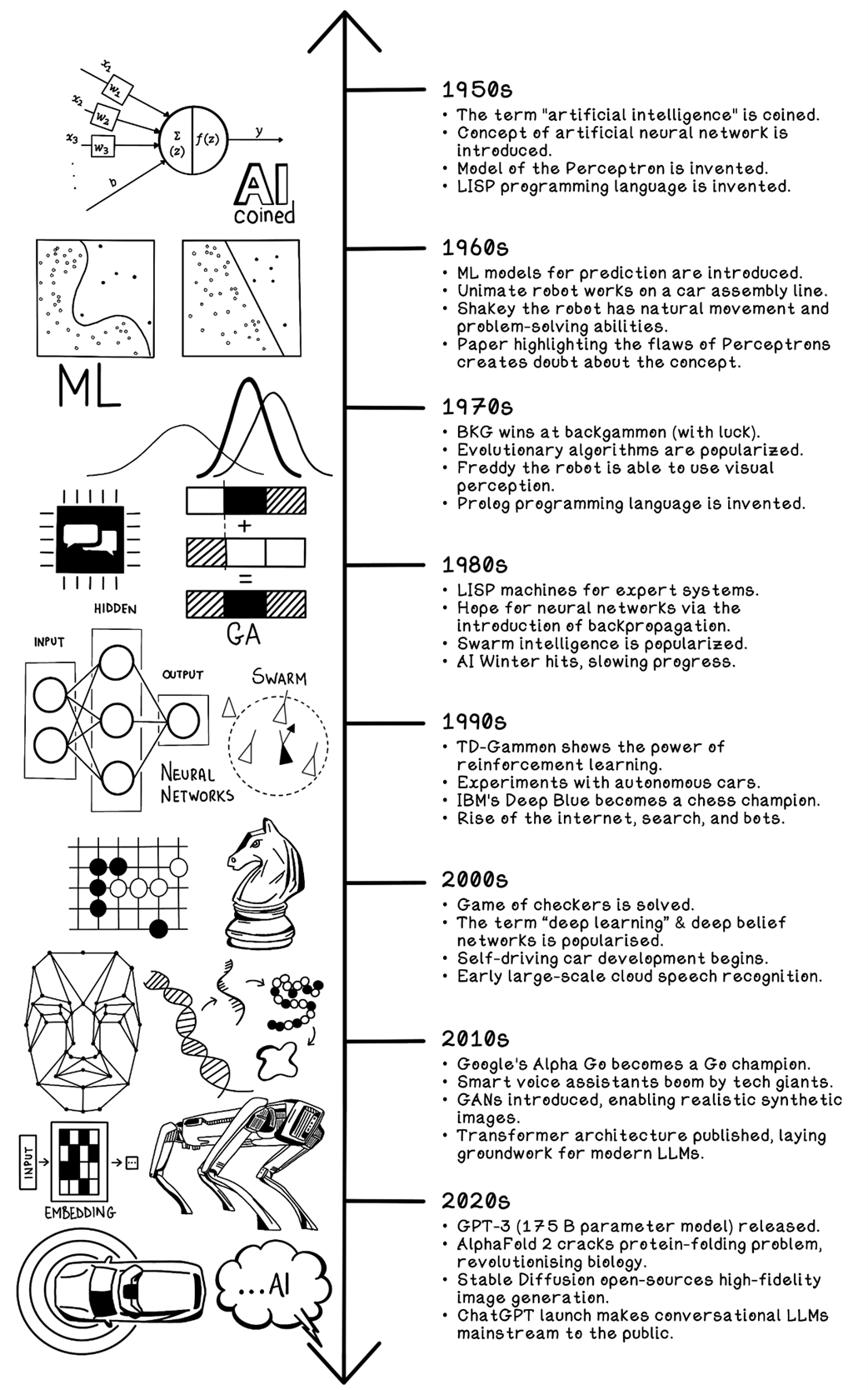
Levels of AI
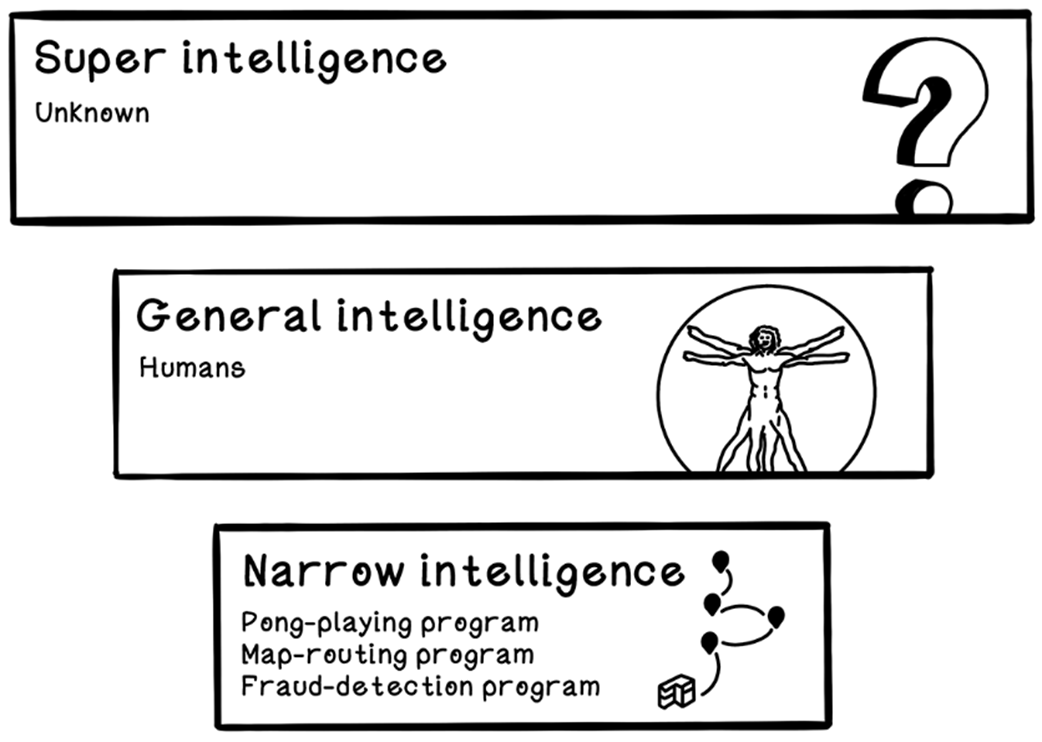
Categorization of concepts within AI
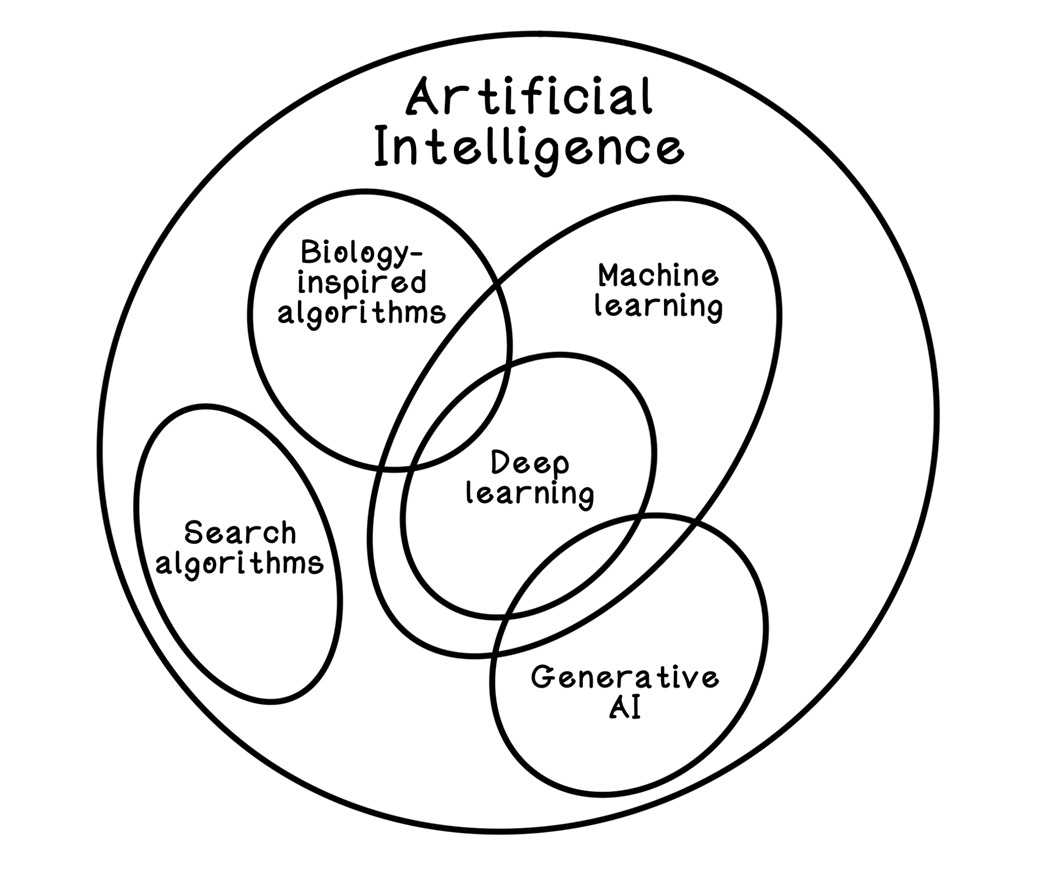
Using data to optimize crop farming
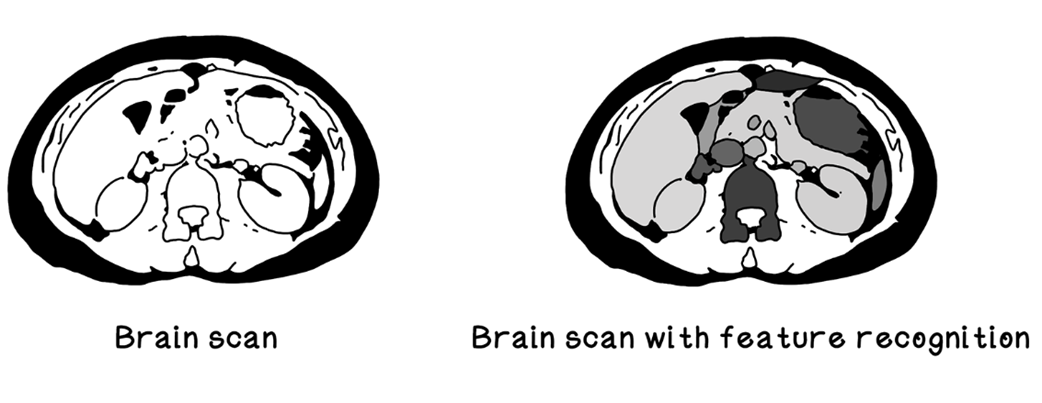
Using machine learning for feature recognition in brain scans
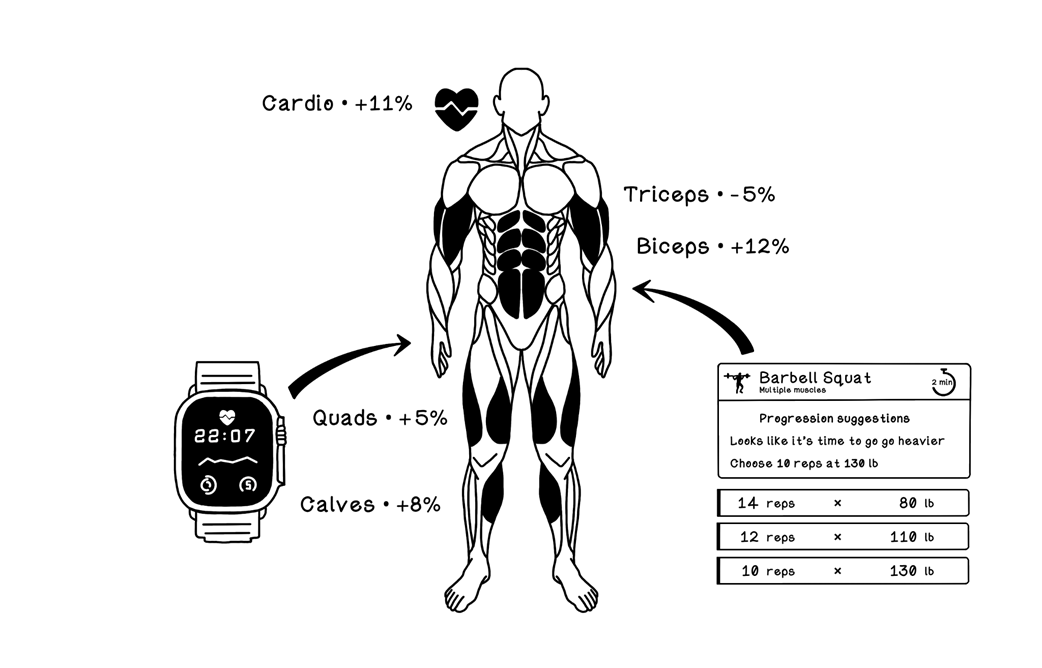
Using sensors and AI to guide fitness & health
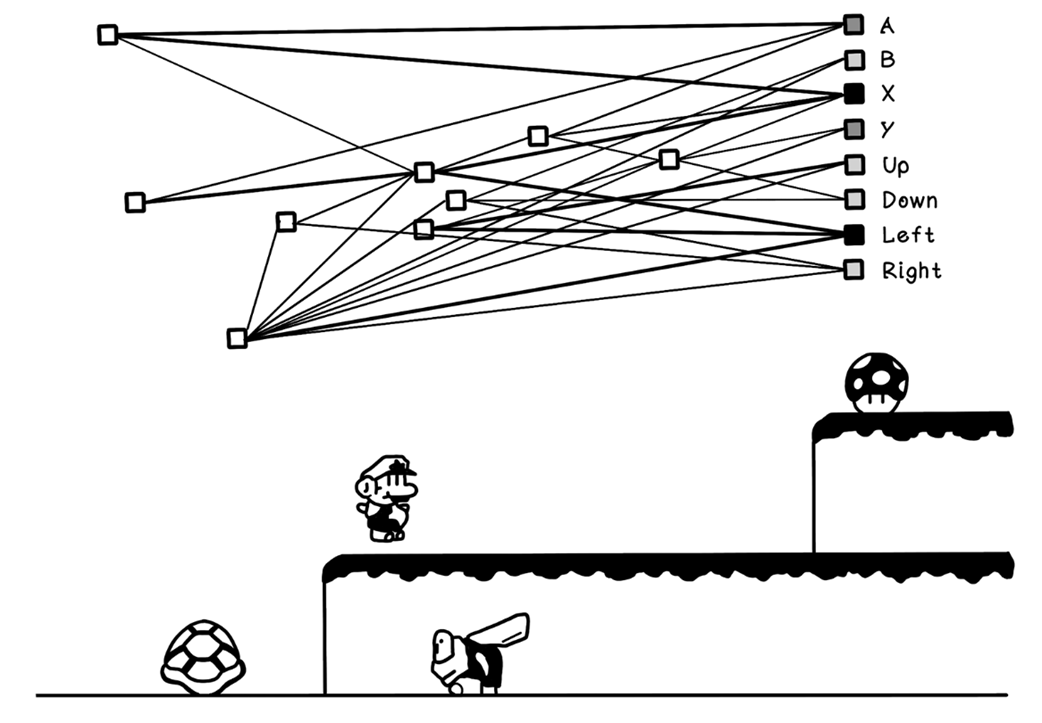
Using neural networks to learn how to play games
Summary of Intuition of AI
FAQ
How does Chapter 1 define Artificial Intelligence?
AI refers to systems that perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence—such as perceiving (vision, hearing), understanding and generating language, reasoning, and decision-making. Two key traits are autonomy (acting without constant instruction) and adaptability (adjusting to changing environments). These systems are powered by data: they take in observations from the world, process them, and act.Why is data called the “fuel” for AI, and how do data, information, and knowledge differ?
Data are raw facts; information is data organized to answer a question; knowledge is the actionable understanding formed by combining information with experience. For example: a temperature reading (data) indicates a fever (information), which suggests treatment (knowledge). Because AI learns patterns from data, poor, biased, or missing data leads to weak outcomes.What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative data, and how can bias arise?
Quantitative data are numeric measurements (for example, temperature), typically gathered with standardized instruments. Qualitative data are descriptive or subjective observations (for example, a movie review). Bias can creep in through sampling choices, context, measurement errors, or how data are recorded and interpreted.What is an algorithm, and why is it compared to a recipe?
An algorithm is a finite set of instructions that transforms inputs into outputs through defined steps. It’s like a recipe: given ingredients and tools (inputs) and a method (steps), you produce a dish (output). Algorithms drive everything from compression and routing to simple programs and games.What’s the difference between an algorithm and a model in AI systems?
Algorithms are the process; models are the artifact. In search, the algorithm actively solves each instance in real time. In machine learning and deep learning, the algorithm “builds” (trains) a model from data; the trained model is then deployed to make predictions or decisions.What types of problems does AI address in this chapter?
- Search problems: Find a path or sequence of actions to reach a goal efficiently.- Optimization problems: Find a good (often near-optimal) solution among many possibilities under constraints; beware local vs global best solutions.
- Prediction: Estimate a numeric value from patterns in data.
- Classification: Assign a label/category based on features.
- Clustering: Discover natural groupings or structure without predefined labels.
How do deterministic and probabilistic models differ?
Deterministic models always produce the same output for the same input (for example, unit conversion). Probabilistic models return outcomes according to a probability distribution; with the same input, repeated runs can yield different results due to controlled randomness (for example, text autocompletion picking among likely next words).What are ANI, AGI, and ASI?
- ANI (Narrow AI): Specialized systems for a single domain; multiple narrow systems can be combined for broader behavior (for example, voice assistants stacking speech, search, and synthesis).- AGI (General AI): Humanlike adaptability—transferring knowledge and reasoning across tasks; still an open challenge.
- ASI (Superintelligence): Intelligence beyond human capability across domains; currently speculative.
What is “old AI” vs “new AI,” and why learn both?
Old AI relies on explicit logic and search (for example, Minimax in games) where humans encode rules and heuristics. New AI learns from data (for example, neural networks trained via self-play or large datasets). Both matter: modern systems often blend them—learning-driven models still use search/optimization to plan or decode efficiently.Which real-world use cases does the chapter highlight for AI?
- Agriculture: Sensor data and models optimize irrigation, fertilization, and yield.- Banking: Anomaly detection flags fraudulent transactions in real time.
- Cybersecurity: NLP-based filters detect phishing beyond simple keywords.
- Health care: Computer vision assists in diagnosing from medical images.
- Logistics: Heuristics and evolutionary/swarm methods find efficient routes and packing.
- Fitness/Health: Wearables feed personalized, adaptive training and recovery advice.
- Games: Search and reinforcement learning master complex strategy and planning.
 Grokking AI Algorithms, Second Edition ebook for free
Grokking AI Algorithms, Second Edition ebook for free