1 Introduction to Bitcoin
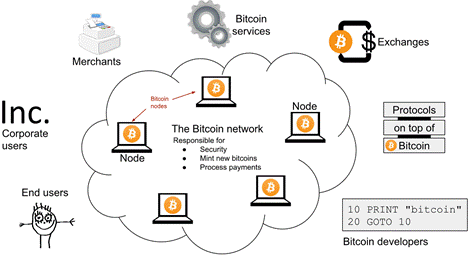
This chapter introduces Bitcoin at a high level and sets expectations for learning how it works and why it matters. Bitcoin is presented as permissionless, decentralized digital cash run by a global network of equal, independent nodes that maintain a shared ledger called the blockchain. Anyone can participate—users, merchants, service providers, exchanges, and developers—and anyone can run a node to verify their own information. A payment flows through four main steps: a user creates and signs a transaction; nodes validate and relay it; miners order transactions into blocks and append them to the blockchain; and wallets notify users while managing private keys. The key idea is that ownership changes by updating the blockchain rather than “sending” coins directly.
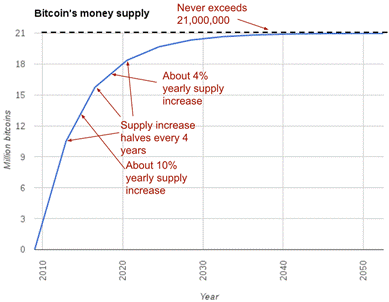
The chapter then contrasts Bitcoin with problems in today’s financial system: billions are unbanked due to cost, documentation, or discrimination; electronic payments can be traced, censored, frozen, or seized; many fiat currencies face inflation or even hyperinflation; and cross‑border transfers are slow and expensive. Bitcoin’s approach tackles these issues by removing central control, treating all participants equally, and making rule changes difficult without broad consensus. It has a strictly limited, predictable supply (capped at 21 million, with issuance declining over time) that resists monetary debasement, and its Internet‑native design makes it borderless, enabling direct global transfer with quick visibility and strong settlement finality. Running your own node eliminates reliance on third parties for transaction verification.
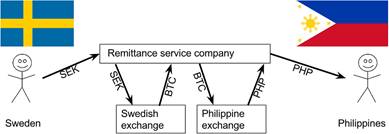
Practical uses covered include savings secured by private keys, cheaper remittances, and shopping without sharing sensitive card data, as well as market‑driven pricing and volatility that fuels speculation. Beyond payments, Bitcoin can anchor proofs (proof of existence) or represent transfers of ownership by embedding small data in transactions. The chapter also notes limits: fees make tiny payments impractical and confirmations add delay, both mitigated by emerging layers such as the Lightning Network; users must manage key security and consider risks like price swings or potential software/cryptography issues. Finally, it surveys other cryptocurrencies and explains how network effects favor Bitcoin’s adoption, motivating the book’s focus on Bitcoin itself.
1. The Bitcoin network and its ecosystem.
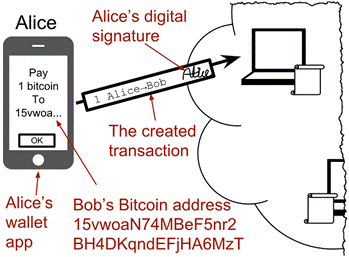
A Bitcoin payment. The payment is processed in 4 steps.

Step 1: Alice creates a transaction, signs it and sends it to one or more Bitcoin nodes in the Bitcoin network.
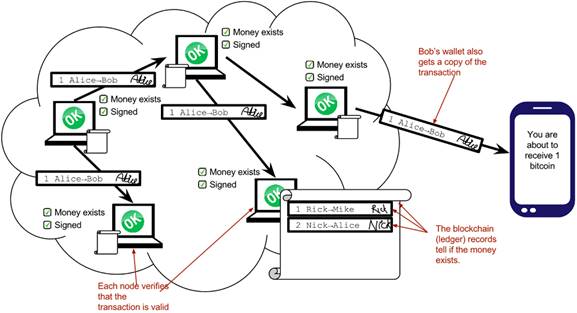
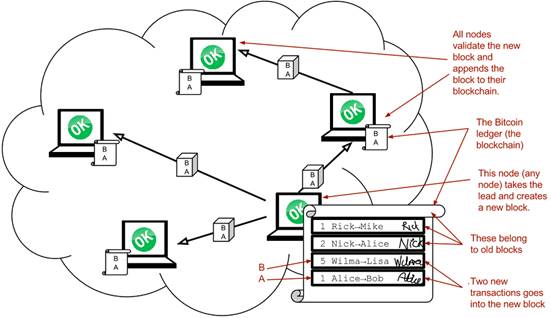
Alice has sent her transaction to a node in the network. The node will verify the transaction and forward it to other nodes. Eventually the transaction has reached all nodes in the network.
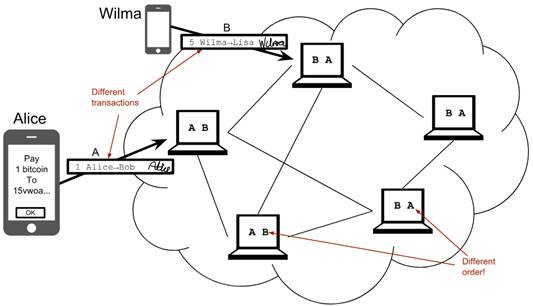
Transactions arrives in different order at different nodes. If they would all write the transactions to the blockchain, the different nodes' blockchains would differ.
One node takes the lead and tells the others what order to add the transactions in. The other nodes verify the block and update their blockchain copies accordingly.
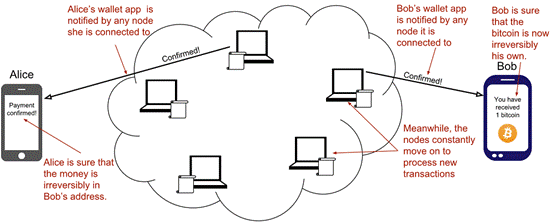
Bob’s wallet have asked a node to notify the wallet upon activity in his Bitcoin address. Alice pays to Bob’s address, and the node has just written the transaction to the blockchain, so it notifies Bob’s wallet.
8. Inflation

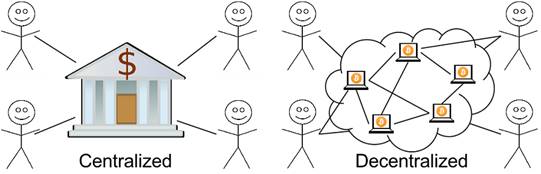
Centralized and decentralized services
The supply of bitcoins over time
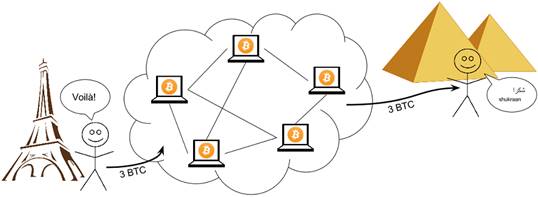
Bitcoin is borderless
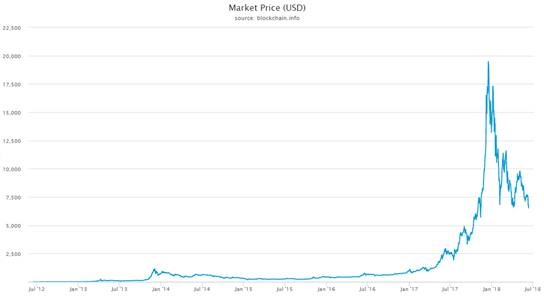
Price in USD since beginning of Bitcoin
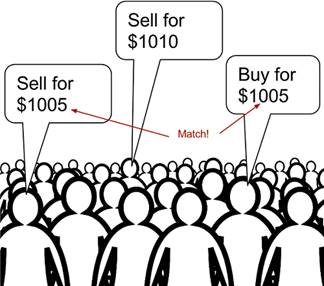
Recap
In this chapter you learned that
- Bitcoin is global, borderless money, that anyone with an internet connection can use.
- Bitcoin is used by many different actors, like savers, merchants, traders for many different purposes like payments, remittances and savings.
- A network of computers, the Bitcoin network, verifies and keeps records of all payments.
- A transaction goes through the steps: Send transaction, verify transaction, add transaction to the blockchain, notify recipient and sender wallet.
- It solves problems with inflation, borders, segregation and privacy by providing limited supply, decentralization and borderlessness.
- There are several alternative cryptocurrencies apart from Bitcoin, for example Ethereum, Zcash and Namecoin.
- A (crypto)currency needs to have enough users and activity to be useful. It’s called network effect.
 Grokking Bitcoin ebook for free
Grokking Bitcoin ebook for free