1 What is machine learning? It is common sense, except done by a computer
This chapter opens by warmly inviting readers into machine learning with the promise that it’s far more approachable than its reputation suggests. Rather than demanding heavy math or nonstop coding, it emphasizes common sense, visual intuition, and curiosity about patterns in data. The author demystifies formulas and code by treating them as languages for expressing simple ideas, noting that the field’s explosive growth comes from abundant data and computing power—and that ML now quietly powers everyday experiences from recommendations to medical support.
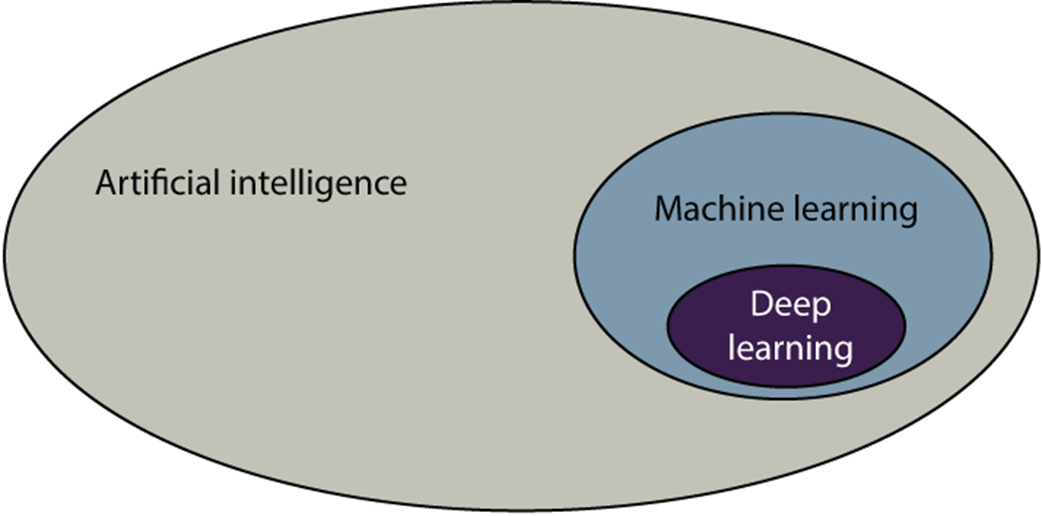
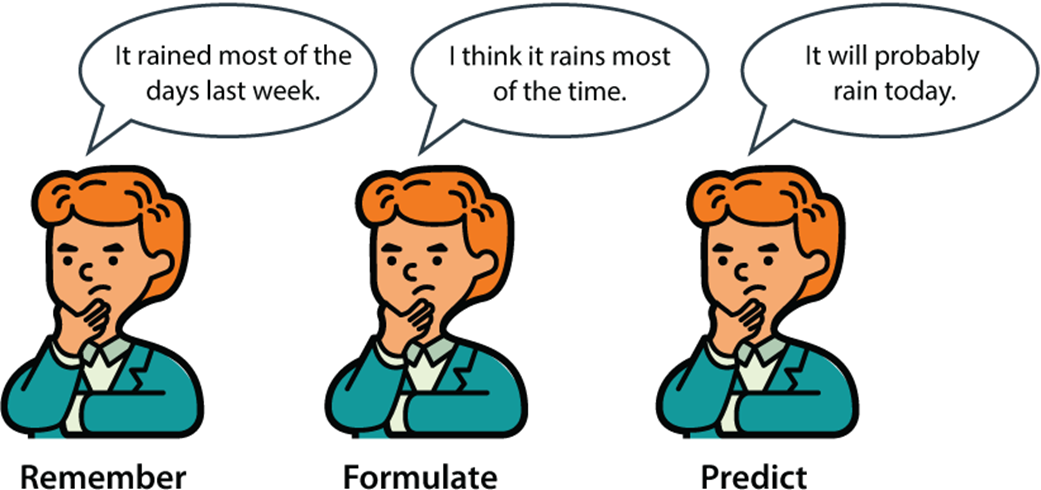
To ground the field, the chapter distinguishes artificial intelligence (computers making decisions), machine learning (computers making decisions from data), and deep learning (a powerful ML subfield using neural networks). It connects ML to how humans decide: we use logic or we rely on experience; ML formalizes the latter. This becomes the remember–formulate–predict framework: remember past data, formulate a rule (a model), and predict on new cases. Along the way, it clarifies core terms—models as decision rules learned from data, algorithms as procedures for building models, and features as the data attributes models use—while stressing that good models are those that generalize to unseen data.
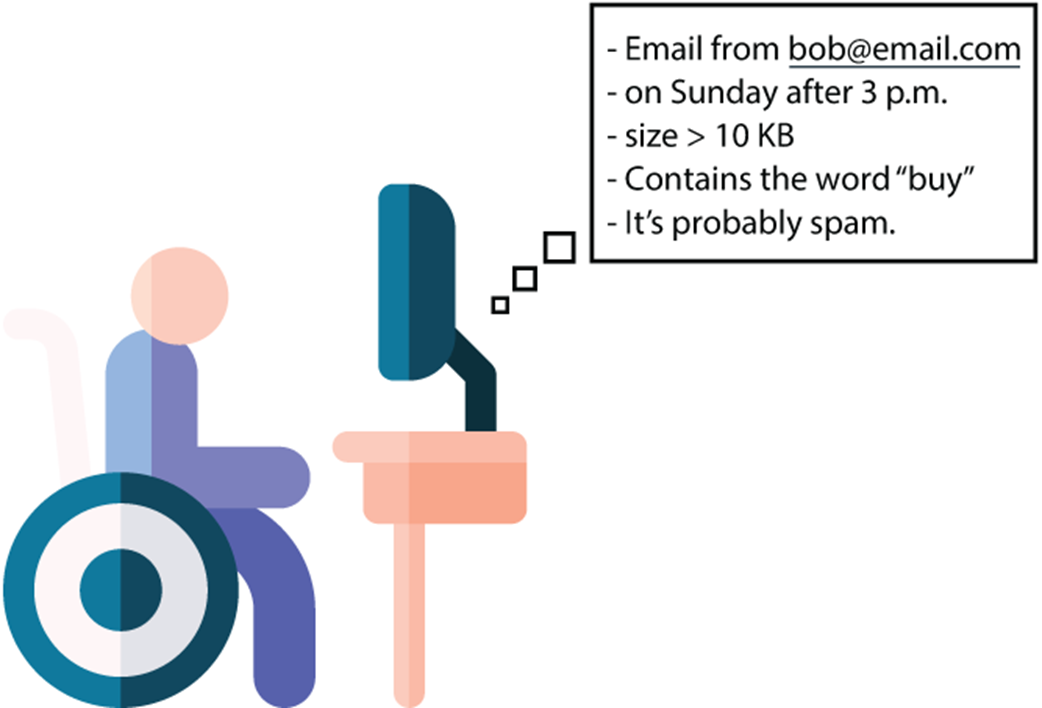
Through a running spam-detection example, the chapter shows how models evolve from simple frequency counts to rules that use informative features (like day of week or email size), then to richer combinations a computer can search efficiently. The lesson is that ML scales this rule-finding process: computers explore many candidate models and select those that fit past data and, ideally, generalize. The chapter closes by contrasting predictive ML (classification and regression) with generative ML (creating text or images), noting that the book focuses on predictive methods—building intuition from scratch implementations before using popular libraries—while offering a glimpse of generative techniques once the foundations are in place.
Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence.
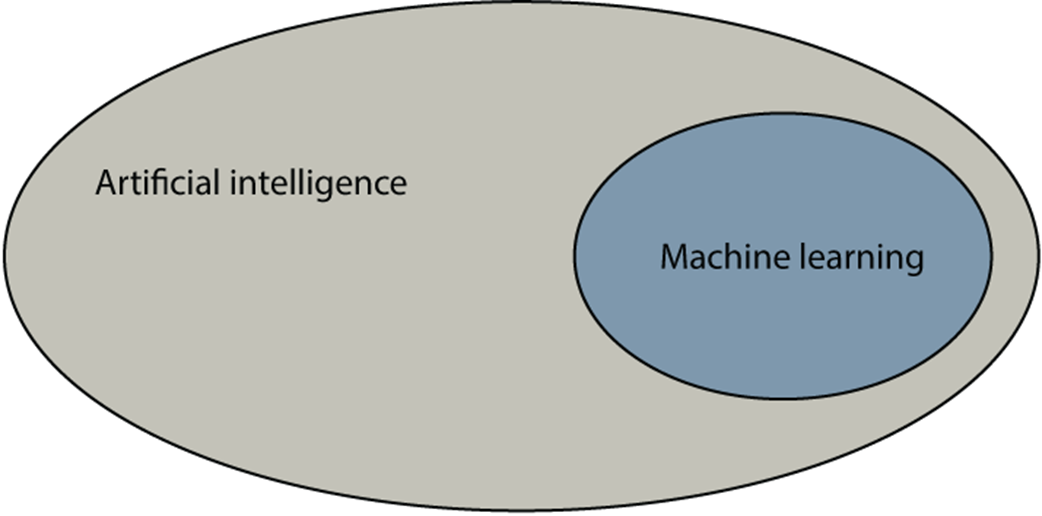
Machine learning encompasses all the tasks in which computers make decisions based on data. In the same way that humans make decisions based on previous experiences, computers can make decisions based on previous data.

Deep learning is a part of machine learning.
The remember-formulate-predict framework is the main framework we use in this book. It consists of three steps: (1) We remember previous data; (2) we formulate a general rule; and (3) we use that rule to make predictions about the future.
A very simple machine learning model
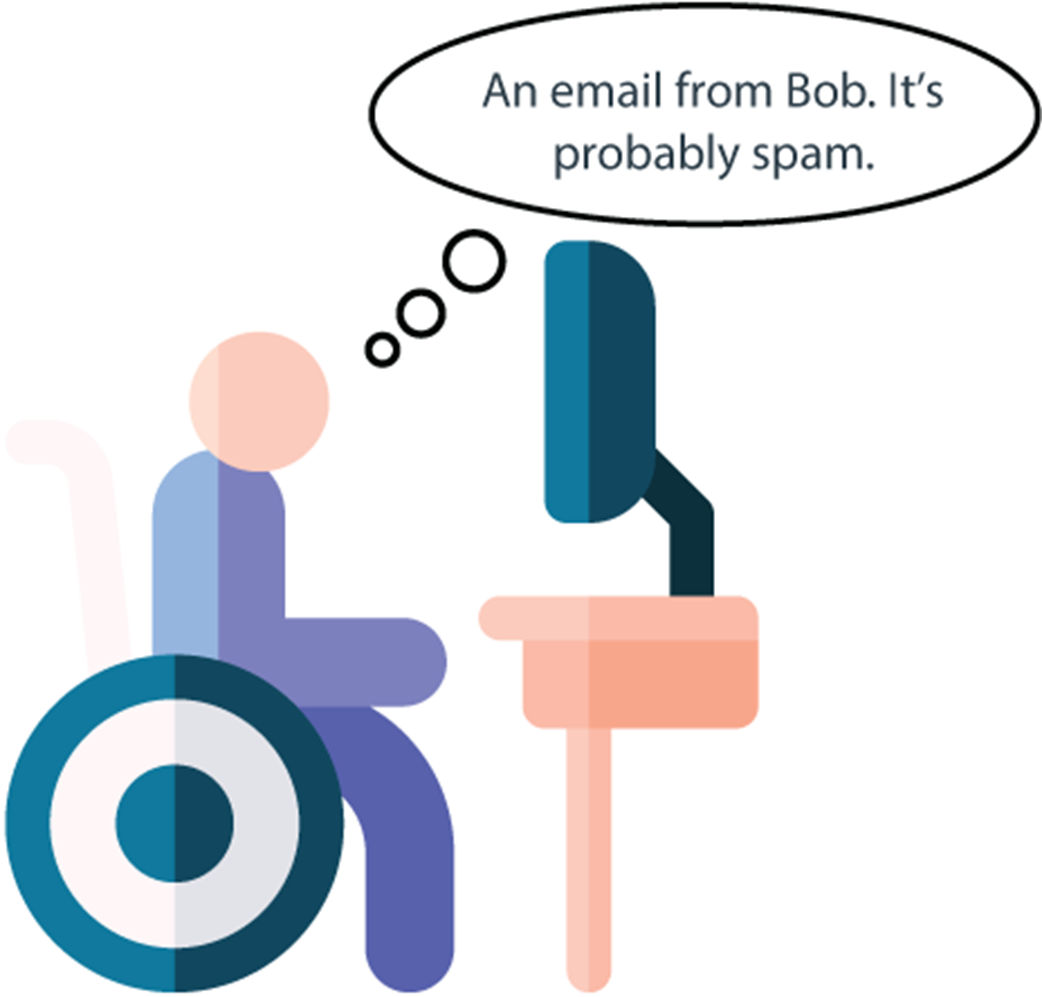
A slightly more complex machine learning model
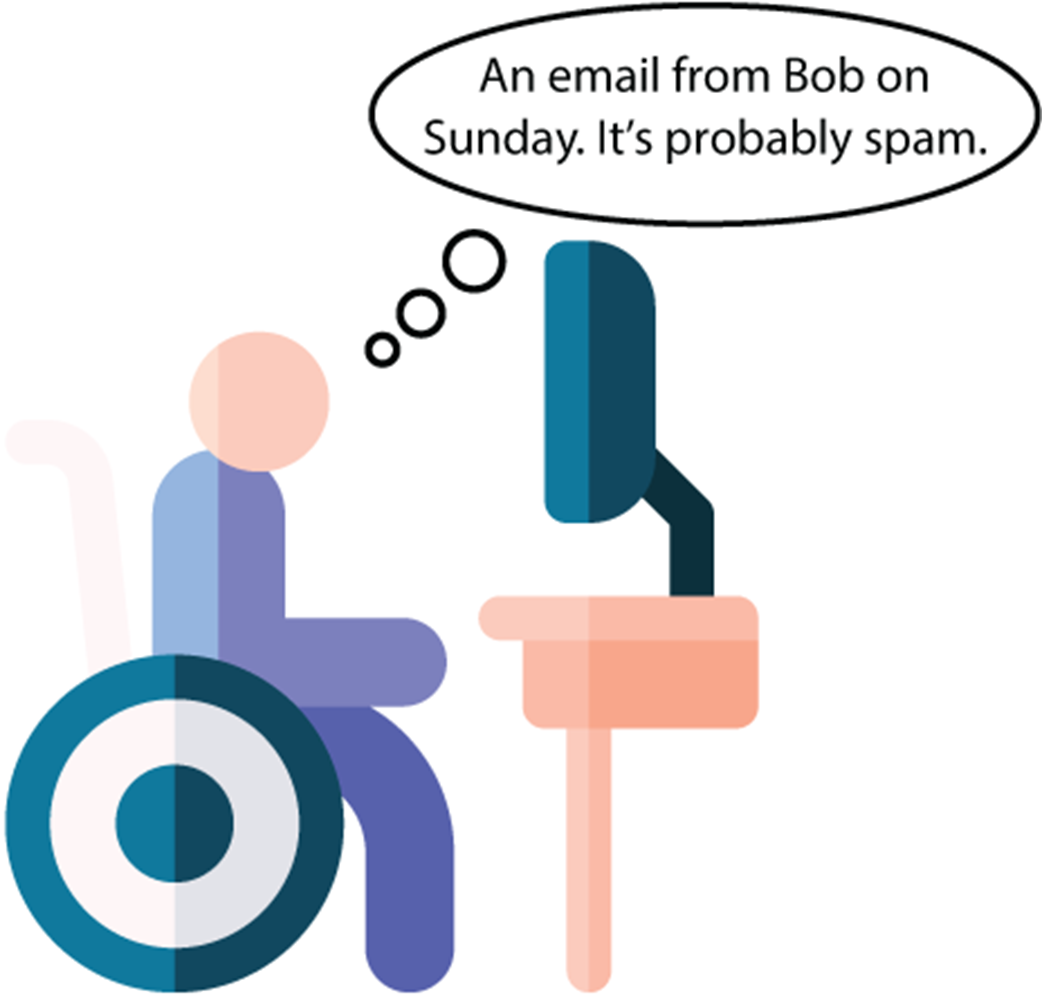
Another slightly more complex machine learning model
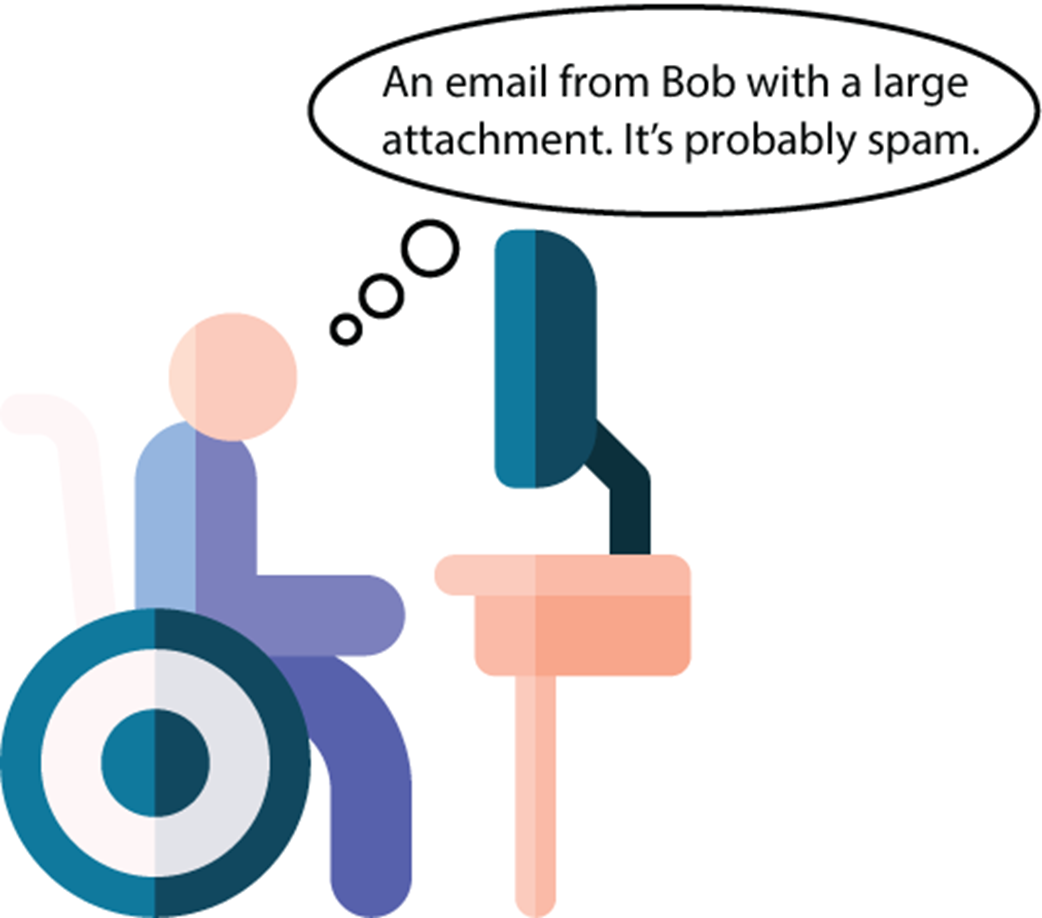
An even more complex machine learning model
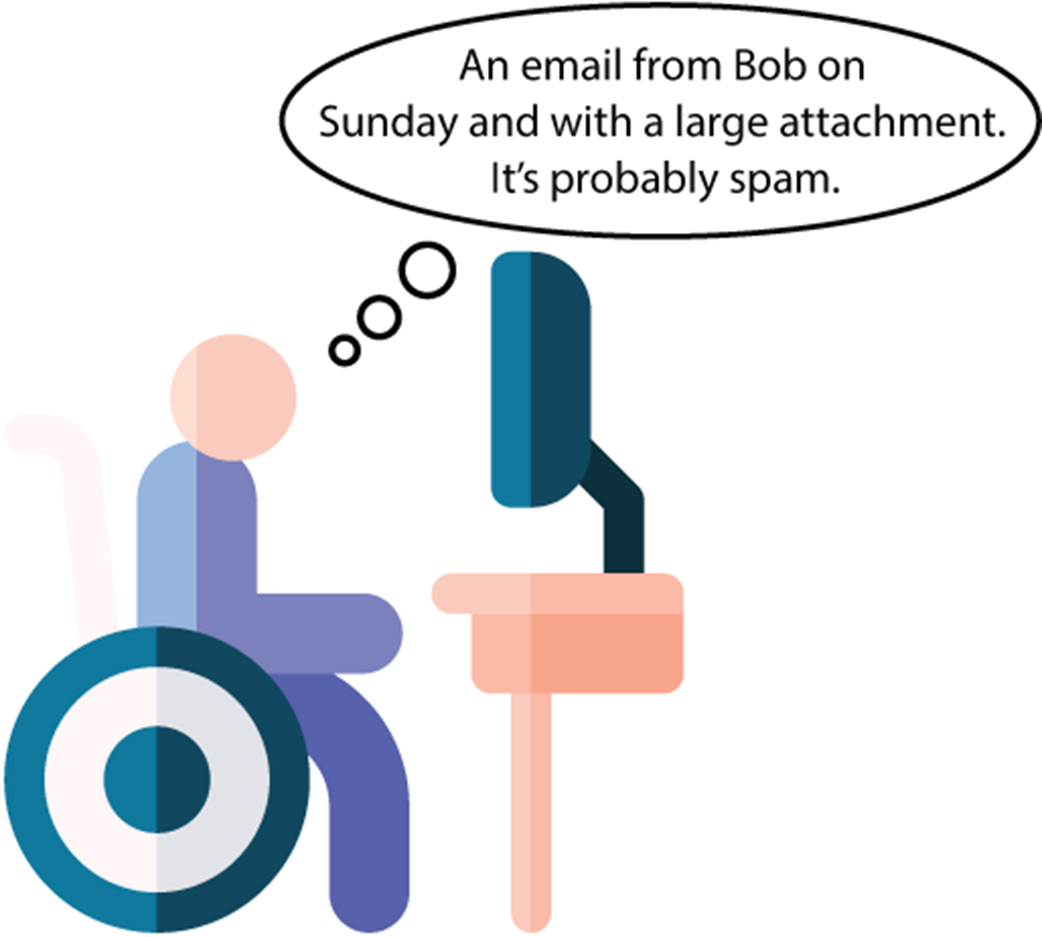
A much more complex machine learning model, found by a computer
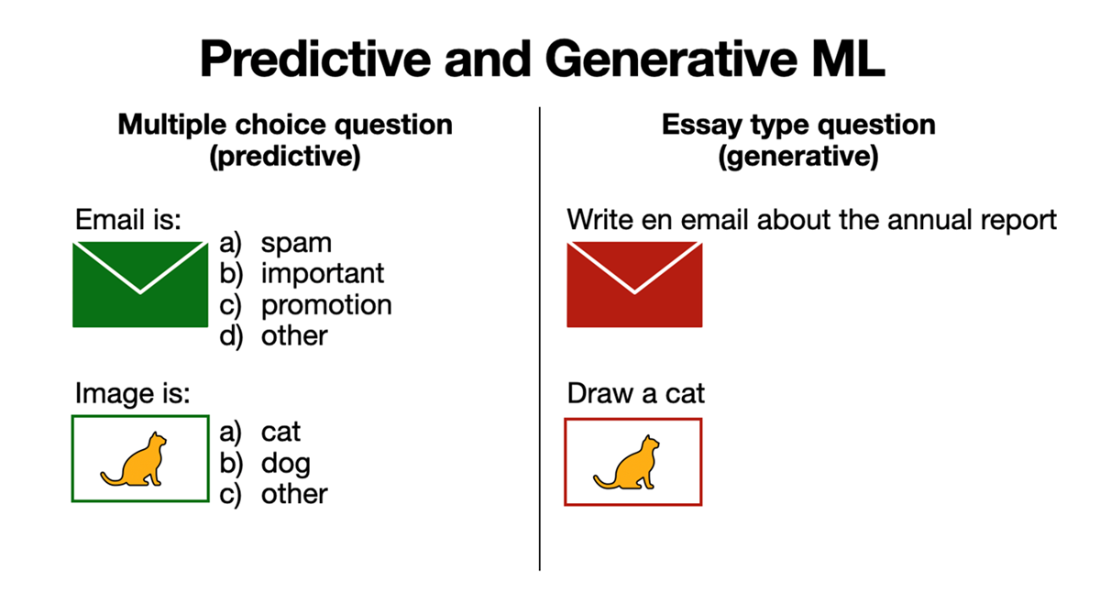
Predictive machine learning is akin to answering questions, such as multiple choice. Generative learning is akin to writing an essay or drawing an image.
Summary
- Machine learning is easy! Anyone can learn it and use it, regardless of their background. All that is needed is a desire to learn and great ideas to implement!
- Machine learning is tremendously useful, and it is used in most disciplines. From science to technology to social problems and medicine, machine learning is making an impact and will continue doing so.
- Machine learning is common sense, done by a computer. It mimics the ways humans think to make decisions quickly and accurately.
- Just like humans make decisions based on experience, computers can make decisions based on previous data. This is what machine learning is all about.
Machine learning uses the remember-formulate-predict framework, as follows:
- Remember: look at the previous data.
- Formulate: build a model, or a rule, based on this data.
- Predict: use the model to make predictions about future data.
 Grokking Machine Learning, Second Edition ebook for free
Grokking Machine Learning, Second Edition ebook for free