Machine learning is presented as a friendly, practical way to make computers solve problems the way people do: by noticing patterns and using common sense—only at machine scale. The chapter reassures readers that ML is widely useful and increasingly accessible; you don’t need heavy math or nonstop coding to get started. Instead, a mix of basic math, visual intuition, and curiosity goes a long way, and formulas or code are treated as languages that become clear when grounded in simple, concrete examples.
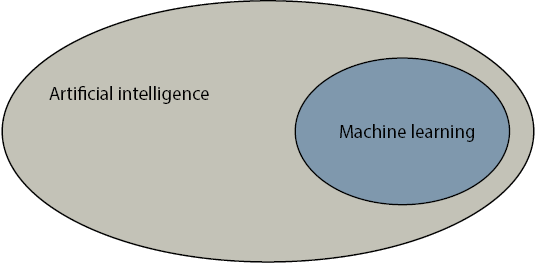
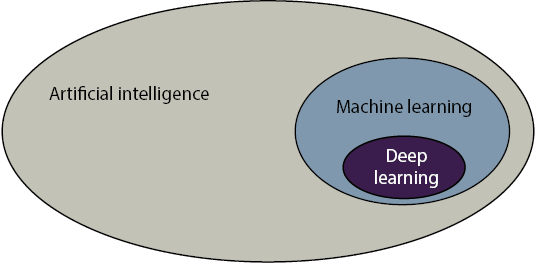
The text clarifies the relationship between AI, machine learning, and deep learning: AI covers any task where computers make decisions; ML is the subset that makes decisions from data (experience); and deep learning is a subset of ML that uses neural networks and powers many state-of-the-art applications. Framing ML as “experience-based” decision-making mirrors how humans often think. This is captured by a simple, recurring process—the remember-formulate-predict framework—where we recall past examples (data), abstract a general rule (model), and use it to forecast outcomes (prediction).
Through a spam-filtering narrative, the chapter shows how models evolve from simple frequency rules to more informative ones using features like day of week, message size, and content signals. It defines key terms: a model is the rule set used to make predictions, an algorithm is the procedure that builds that model, and features are the data properties models rely on. The payoff of ML is that computers can sift through many candidate rules—logical combinations or weighted formulas—to find those that fit data well and, crucially, generalize to new cases. The chapter sets the stage for learning how to evaluate and improve such models, moving from hand-built intuition to scalable, computer-assisted discovery.
Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine learning encompasses all the tasks in which computers make decisions based on data. In the same way that humans make decisions based on previous experiences, computers can make decisions based on previous data.

Deep learning is a part of machine learning.
The remember-formulate-predict framework is the main framework we use in this book. It consists of three steps: (1) We remember previous data; (2) we formulate a general rule; and (3) we use that rule to make predictions about the future.

A very simple machine learning model

A slightly more complex machine learning model

Another slightly more complex machine learning model

An even more complex machine learning model

A much more complex machine learning model, found by a computer

Summary
- Machine learning is easy! Anyone can learn it and use it, regardless of their background. All that is needed is a desire to learn and great ideas to implement!
- Machine learning is tremendously useful, and it is used in most disciplines. From science to technology to social problems and medicine, machine learning is making an impact and will continue doing so.
- Machine learning is common sense, done by a computer. It mimics the ways humans think to make decisions quickly and accurately.
- Just like humans make decisions based on experience, computers can make decisions based on previous data. This is what machine learning is all about.
Machine learning uses the remember-formulate-predict framework, as follows:
- Remember: look at the previous data.
- Formulate: build a model, or a rule, based on this data.
- Predict: use the model to make predictions about future data.
 Grokking Machine Learning ebook for free
Grokking Machine Learning ebook for free