1 Introduction to Hugging Face
This chapter introduces Hugging Face as a collaborative, open-source hub for building, training, and deploying modern machine learning models. It highlights how the platform unifies community-driven models and datasets with practical developer tools across natural language, computer vision, and audio. By providing ready-to-use components and hosted resources, Hugging Face enables developers to focus on solving real problems and shipping applications rather than constructing models from scratch, all while advancing an open, shared ecosystem.
The chapter spotlights the Transformers library and its pipeline API, which make tasks like sentiment analysis, translation, summarization, and object detection accessible with minimal code and pre-trained checkpoints. It also tours the Model Hub, where repositories expose rich documentation, usage snippets, and interactive widgets, and explains the Hosted Inference API for instant, scalable testing alongside options for local execution. Complementing these, Gradio offers a fast way to wrap functions and models in web interfaces, and together with Spaces, simplifies prototyping, demoing, and sharing ML apps with users.
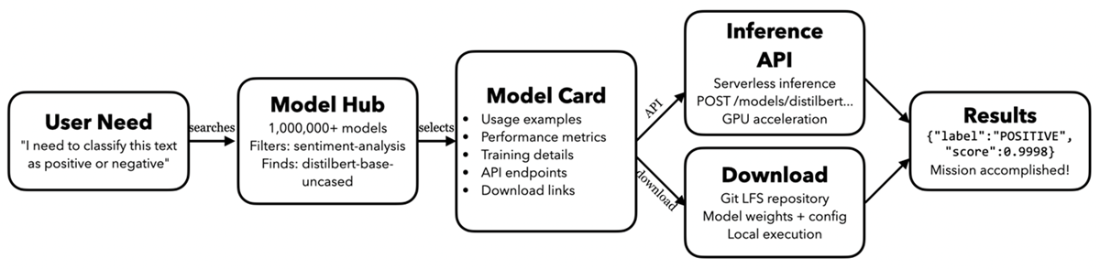
Finally, the chapter presents a practical mental model for solving problems on Hugging Face: begin with a clear need, discover a suitable model via robust search and filters, use the model card as the bridge from evaluation to implementation, choose either the hosted Inference API or local deployment, and deliver results. It also previews advanced topics covered later in the book, including building LLM applications with orchestration frameworks and visual tools, evaluating open alternatives to popular models, protecting data privacy in LLM workflows, creating tool-using agents, and connecting assistants to external data through standardized protocols.
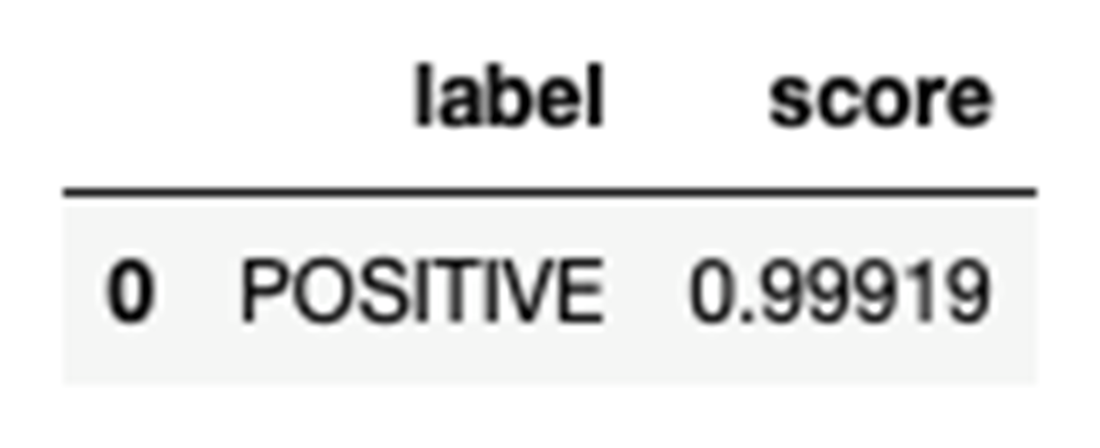
The result of the sentiment analysis
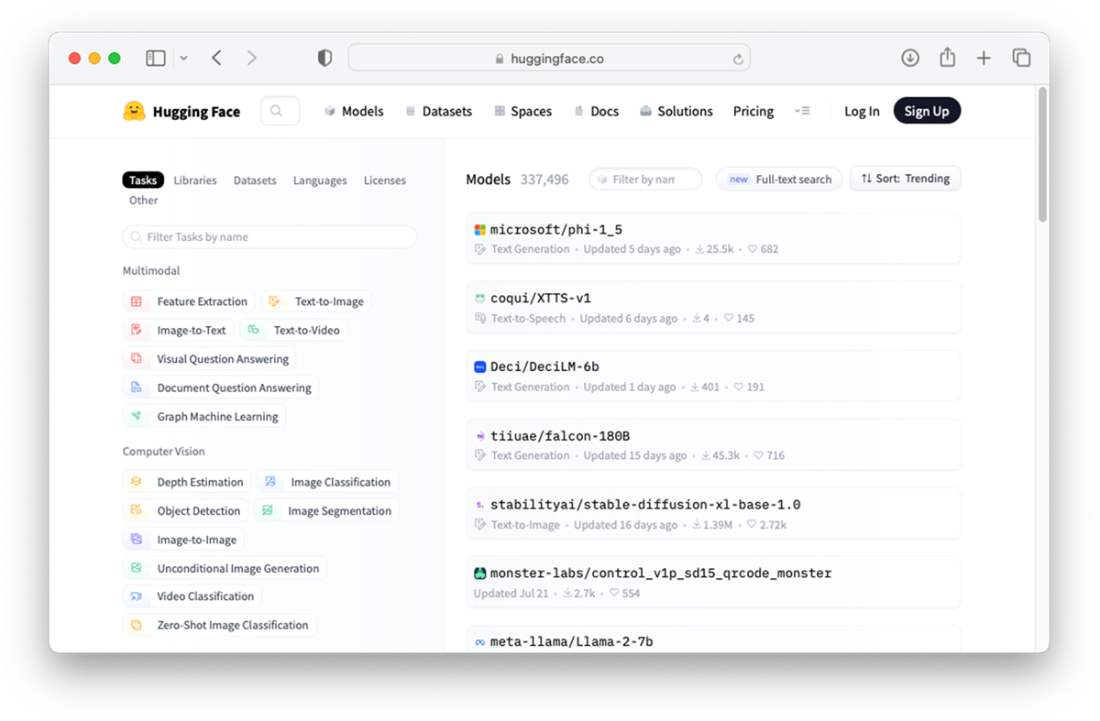
Exploring the pre-trained models hosted on Hugging Face hub
You can test the model directly on Hugging Face hub using the Hosted inference API
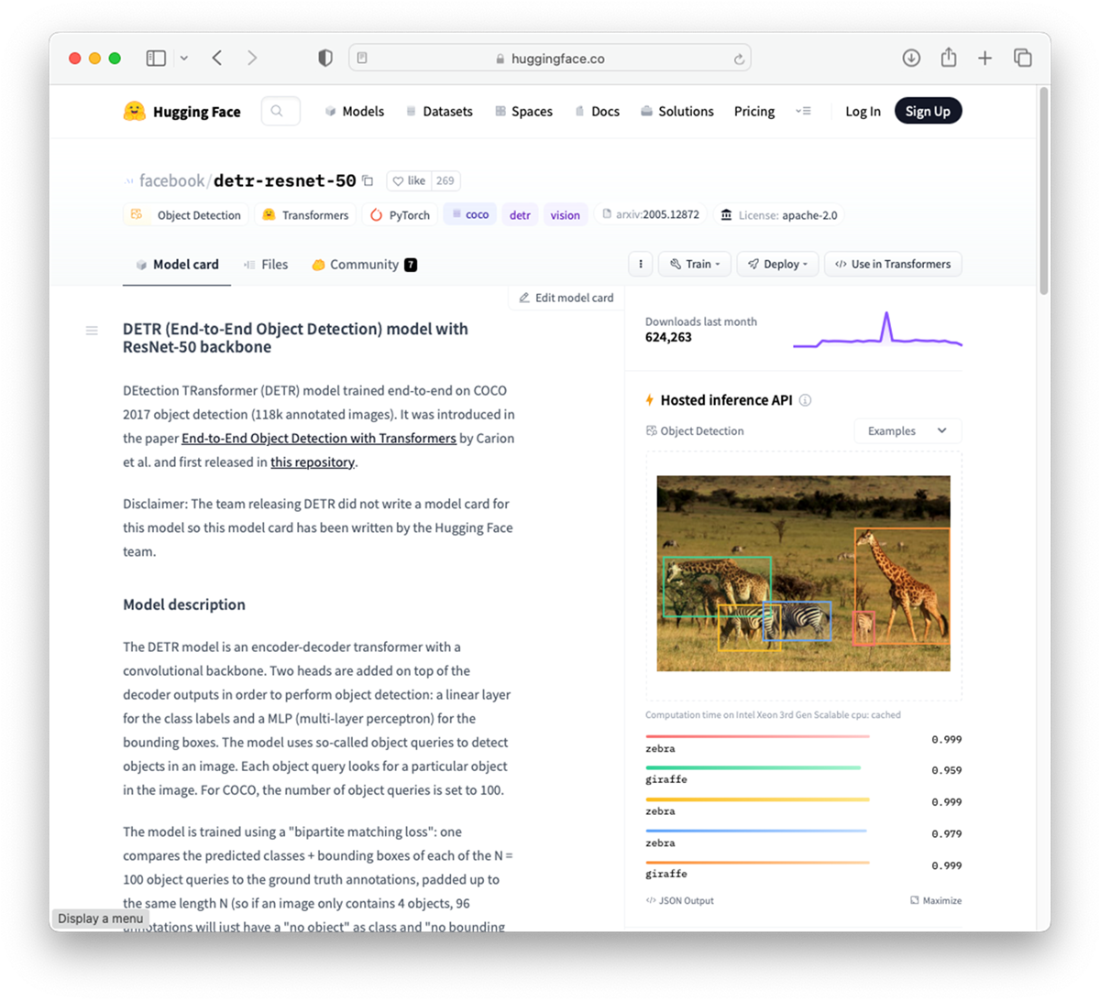
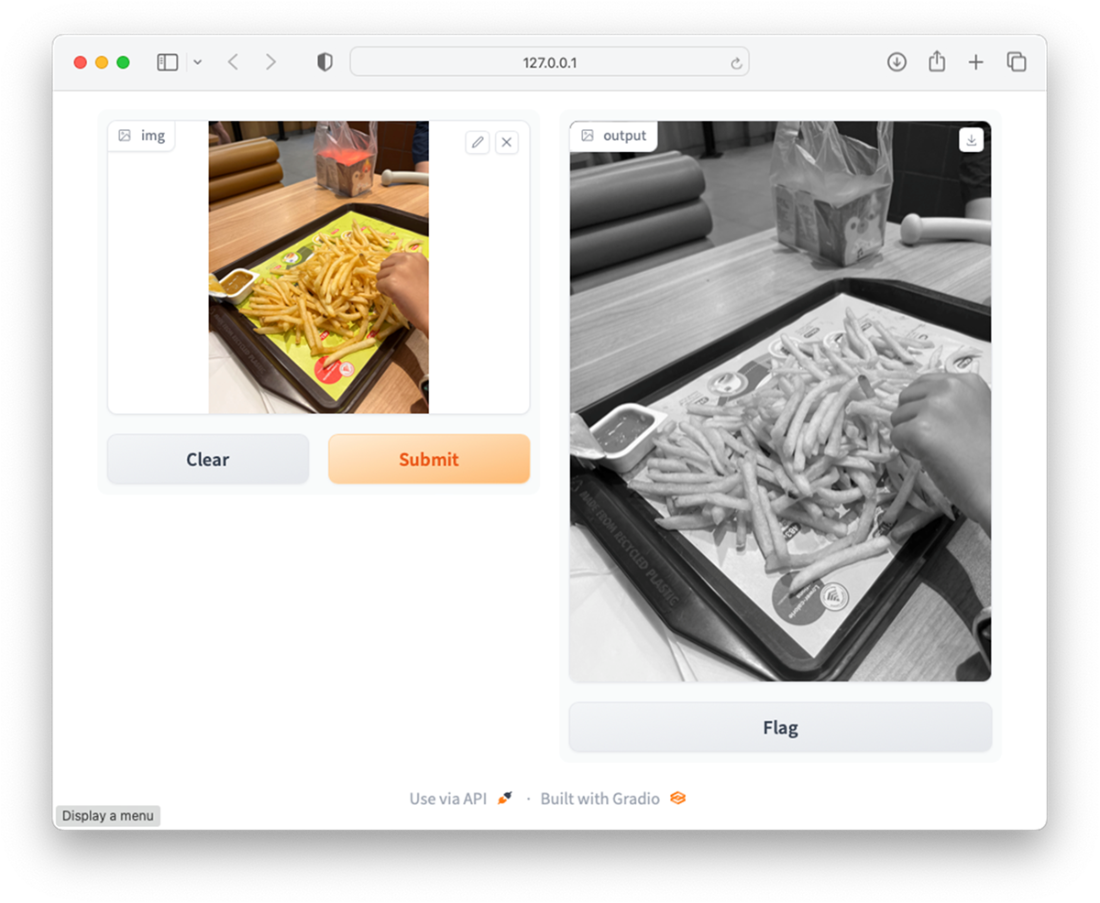
Performing object detection using my uploaded image

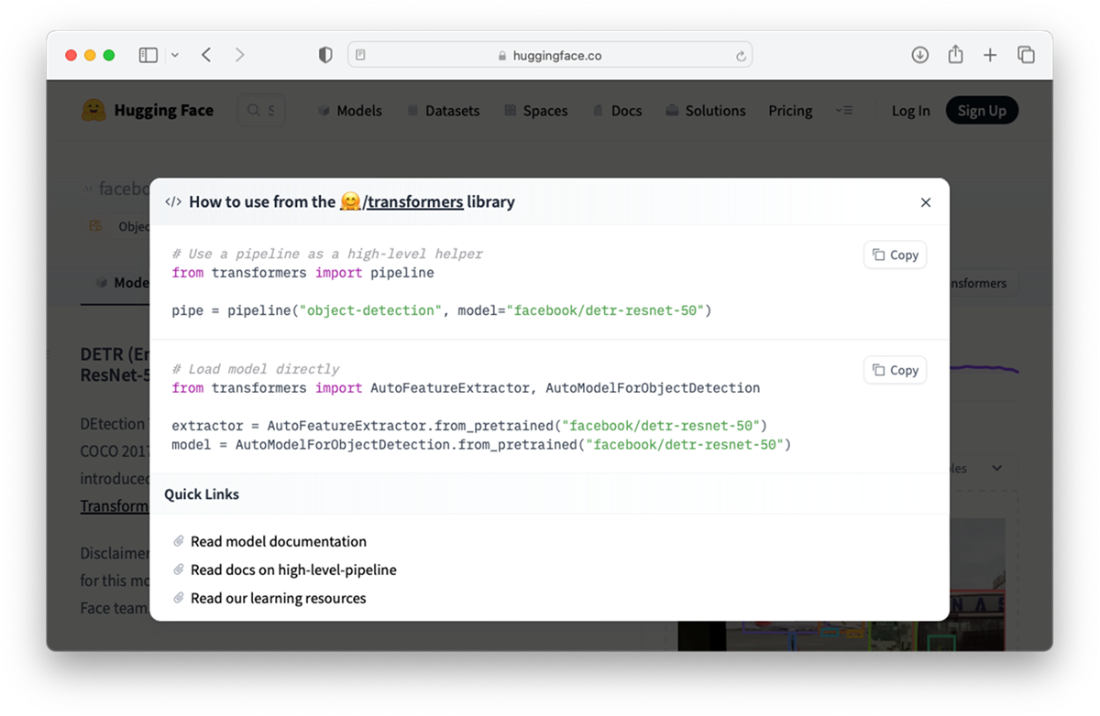
Locating the “</> Use in Transformers” button
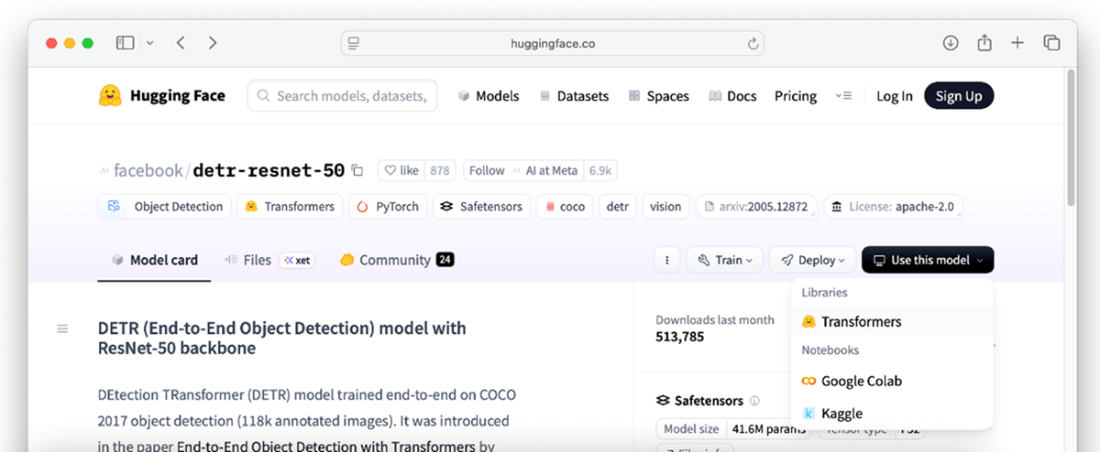
Using the model using the transformers library
Gradio provides a customizable UI for your ML projects
Viewing the result of the converted image
A visual mental model showing Hugging Face’s core process
Summary
- The Transformers Library is a Python package that contains open-source implementation of the Transformer architecture models for text, image, and audio tasks.
- In Hugging Face's Transformers library, a pipeline is a high-level, user-friendly API that simplifies the process of building and using complex natural language processing (NLP) workflows.
- The Hugging Face Hub’s Models page hosts many pre-trained models for a wide variety of machine learning tasks.
- Gradio is a Python library that creates a Web UI that you can use to bind to your machine learning models, making it easy for you to test your models without spending time building the UI.
- Hugging Face isn’t just a model repository. It’s a complete AI problem-solving pipeline that systematically moves users from problems to solution.
FAQ
What is Hugging Face and what is it best known for?
Hugging Face is an AI community and platform focused on open-source machine learning. It’s known for the Transformers library, the Hub for hosting models and datasets, Hugging Face Spaces for sharing apps, and the Gradio library for building quick ML UIs.What is the Transformers library and why should I use it?
Transformers is a Python library with state-of-the-art Transformer models for text, image, and audio tasks. It lets you download and use pre-trained models via simple APIs, so you can solve tasks without training models from scratch.What is a pipeline in Transformers?
A pipeline is a high-level API that lets you perform tasks like text classification, named entity recognition, translation, and summarization with just a few lines of code, handling preprocessing, model inference, and postprocessing for you.How can I run a quick sentiment analysis with a pre-trained model?
- Import and create a pipeline for text classification using a pre-trained model, then pass text to it.Example:
from transformers import pipeline
classifier = pipeline('text-classification',
model='distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english',
revision='af0f99b')
result = classifier("Your review text here")What is the Hugging Face Model Hub and how do I find the right model?
The Model Hub hosts over a million pre-trained models. You can search and filter by task (e.g., sentiment analysis, translation), architecture (e.g., BERT, GPT, ResNet), language, and metrics to quickly find a model that fits your problem.What is a Model Card and why does it matter?
A Model Card is a model’s documentation page. It includes usage examples (copy-paste code), training details, benchmarks, intended use, and limitations—bridging the gap between discovering a model and implementing it correctly.What is the Hosted Inference API and when should I use it?
The Hosted Inference API lets you run inferences via simple HTTP requests against models hosted on Hugging Face infrastructure—no setup required. Use it for fast prototyping, evaluation, and lightweight production needs. For full control, download and run models locally with Transformers.How can I try an object detection model like facebook/detr-resnet-50 in the browser?
Open the model’s page on the Hub, use the built-in widget under the Hosted Inference section, and drag-and-drop an image. The page will run inference and display detected objects with confidence scores.What is Gradio and how does it help me share my models?
Gradio is an open-source Python library that builds web UIs for ML functions in minutes. Users can upload inputs (text, images, audio) and see outputs instantly. It integrates with Hugging Face Spaces so you can host and share interactive demos publicly.What is the Hugging Face mental model for going from need to results?
- Step 1: Define the user need (e.g., classify sentiment, translate text).- Step 2: Discover a suitable model on the Hub using filters and search.
- Step 3: Read the Model Card for usage and guidance.
- Step 4: Choose execution path: Hosted Inference API or local/own infra via Transformers.
- Step 5: Get results (e.g., {"label":"POSITIVE","score":0.9998}) and solve the task.
 Hugging Face in Action ebook for free
Hugging Face in Action ebook for free