Modern systems are increasingly polyglot and distributed, which makes fast, reliable, language-agnostic communication essential. Apache Thrift addresses this by unifying type serialization and service implementation through a single, vendor-neutral framework. Developers describe data and services once in an Interface Definition Language (IDL), generate code for many languages, and gain built-in support for interface evolution. Thrift’s modular design lets teams choose protocols (binary, compact, JSON) and transports (sockets, files, in-memory, layered options like compression or encryption), and deploy lightweight, prebuilt servers that suit microservices, containers, and embedded environments.
The chapter demonstrates these ideas by building a tiny cross-language “hello” microservice. A small IDL defines a one-function service, the Thrift compiler generates client and server stubs, and a minimal Python server is assembled using provided transports, protocols, and a simple server shell. Clients in Python, C++, and Java communicate with identical I/O stacks and nearly identical code structure, highlighting Thrift’s consistent meta-model across languages and its ability to minimize boilerplate. Together with schema-first design and evolution features, Thrift enables teams to iterate safely in CI/CD pipelines while keeping services small, fast, and easy to integrate.
The chapter also situates Thrift among alternatives. SOAP and REST offer broad reach over HTTP with human-readable payloads, but carry more overhead and variability; Protocol Buffers provides a comparable schema system with RPC options like gRPC; Avro commonly targets on-disk serialization. Thrift’s strengths are its complete in-tree package (IDL, codegen, transports, protocols, and servers), high performance without HTTP, broad language and platform reach, pluggability, and a rich, expressive IDL—all backed by an active open-source community. The result is a pragmatic choice for high-performance, cross-language services that still offers pathways to integrate with web and mobile ecosystems when needed.
The Tiobe Index uses web search results to track programming language popularity (http://www.tiobe.com).
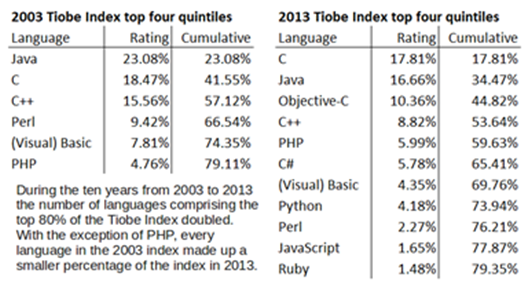
Figure1.2 Efficient translators are a core asset of any multi-language assembly.

Apache Thrift can be used to serialize data in cross-platform messaging scenarios.
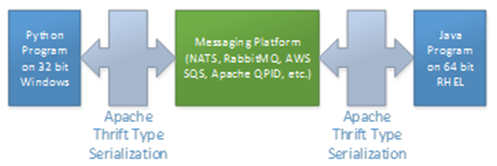
The Apache Thrift RPC framework enables cross-platform services.
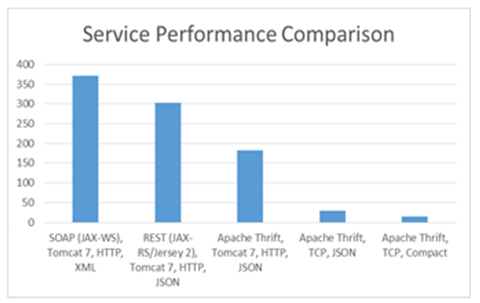
Time to complete 1 million service requests for various Java servers
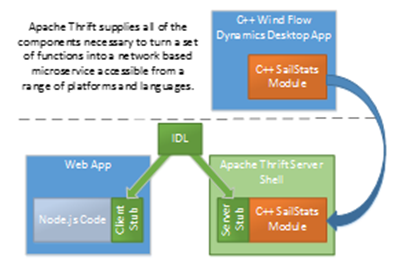
Apache Thrift balances performance with reach and flexibility.

Apache Thrift is an effective solution in embedded, enterprise, and web technology environments.

Summary
Here are the most important points to take away from this chapter:
- Apache Thrift is a cross-language serialization and service implementation framework.
- Apache Thrift supports a wide array of languages and platforms.
- Apache Thrift makes it easy to build high performance services.
- Apache Thrift is a good fit for service-oriented and microservice architectures.
- Apache Thrift is an Interface Definition Language (IDL)-based framework.
- IDLs allow you to describe interfaces and generate code to support the interfaces automatically.
- IDLs allow you to describe types used in messaging, long-term storage, and service calls.
- Apache Thrift includes a modular serialization system, providing several built-in serialization protocols and support for custom serialization solutions.
- Apache Thrift includes a modular transport system, providing built-in memory and disk and network transports, yet makes it easy to add additional transports.
- Apache Thrift supports interface evolution empowering CI/CD environments and Agile teams.
FAQ
What is Apache Thrift and why was it created?
Apache Thrift is an open-source framework for defining data types and remote services in a language-neutral IDL, then generating cross-language code to serialize data and perform RPC. It was built to let teams create small, fast, interoperable services across many languages and platforms with minimal boilerplate.How does Thrift enable polyglot systems? Which languages does it support?
Thrift provides one IDL that you compile into client/server stubs for many languages, ensuring consistent types and behavior across the stack. It supports 20+ languages (for example C/C++, Java, C#, Go, Python, JavaScript/TypeScript, PHP, Ruby, Rust, Objective‑C, Haskell, Erlang, Dart, Lua, and more), with active community additions.What are the two core concerns Thrift addresses in inter-process communication?
- Type serialization: reliably encoding/decoding structured data across languages and platforms.- Service implementation: defining services and generating client/server stubs so calls can be made over the network as if they were local.
Why isn’t plain JSON enough for cross-language messaging?
JSON describes data layout but not the full contract: field numbering/ordering, missing/extra fields, type mapping, and evolution rules vary by implementation. Thrift adds a formal schema (IDL) and generated code that enforces consistent serialization/deserialization across languages; you can still choose a JSON protocol if you want human-readable payloads.What is Thrift IDL and why use it instead of a schemaless approach?
Thrift IDL is a concise, language-neutral definition of types and services. Benefits:- A single source of truth for interfaces and data.
- Fast, correct code generation for many languages.
- Easier design discussion and change review.
- Safer evolution than relying on implicit, undocumented schemas.
How does Thrift support interface evolution without breaking clients?
Thrift uses stable field IDs and optional/required semantics so you can add, remove, or change fields with backward/forward compatibility. Multiple interface versions can coexist, enabling incremental, CI/CD-friendly rollouts instead of “big bang” redeployments.What are Thrift protocols and transports? Can they be layered?
- Protocols: pluggable serializers (binary for speed, compact for size, JSON for readability).- Transports: pluggable I/O (TCP sockets, UNIX domain sockets, named pipes, files, memory, etc.).
- Layering: you can stack transports (for example, buffering, compression like zlib, logging, encryption) to add capabilities without changing your IDL.
What are Thrift’s prebuilt server shells and when should I use them?
Thrift ships lightweight, ready-to-use servers in many languages (for example, simple, threaded, nonblocking). They let you host services without building a custom network stack, use far less memory than full app servers, and fit well in containers and embedded environments.How do I create a simple Thrift microservice and client?
- Define your service and types in a .thrift file.- Run the thrift compiler to generate language-specific stubs.
- Implement a handler class with your service methods.
- Pick a protocol and transport; start a prebuilt server with your processor/handler.
- In clients, create the same protocol/transport stack, instantiate the generated client, open the transport, call methods, and close.
How does Thrift compare with REST, SOAP, Protocol Buffers/gRPC, and Avro? When should I choose it?
- REST: great reach and ecosystem; human-readable; higher overhead for backend RPC. Thrift is faster and smaller for internal services.- SOAP: interoperable but heavy XML/HTTP stack; Thrift is simpler and much faster.
- Protocol Buffers/gRPC: similar serialization; gRPC uses HTTP/2. Thrift offers in-tree RPC, modular protocols/transports, and very broad language/server support.
- Avro: schema travels with data; popular for storage/streaming. Thrift is more commonly used for real-time RPC.
Choose Thrift for high-performance, cross-language microservices with a small footprint and flexible protocol/transport options; choose REST for public web APIs or when HTTP-native behavior and human-readable payloads are priorities.
 Programmer’s Guide to Apache Thrift ebook for free
Programmer’s Guide to Apache Thrift ebook for free