1 Overview
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a method for injecting human preferences into AI systems to handle objectives that are hard to specify explicitly. It rose to prominence by enabling conversational models to move from raw next-token completion to helpful, safe, and engaging dialogue, becoming a cornerstone of modern “post-training.” At a high level, RLHF helps models internalize the style, tone, and behavioral norms people prefer across domains, turning broadly capable base models into reliable, general-purpose assistants.
The canonical RLHF pipeline has three stages: instruction/supervised fine-tuning to teach basic instruction following, reward modeling from human preference data, and reinforcement learning to optimize model responses against the learned reward. In today’s post-training stack, RLHF largely occupies preference fine-tuning, complemented by instruction/SFT and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). Unlike per-token instruction tuning, RLHF adjusts behavior at the whole-response level using contrastive signals (better vs. worse responses), which tends to generalize more robustly across tasks. This power comes with costs and risks: reward models are proxy objectives, training can over-optimize or induce biases (like length bias), and the process is compute-, data-, and operations-intensive. As a result, RLHF is most effective as part of a multi-stage post-training recipe built on a strong base model.
The field has evolved from early instruction-tuned, vibes-driven open models to broader acceptance of preference optimization, including simpler algorithms like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), while closed labs advanced multi-stage post-training at scale. A useful mental model is the “elicitation” view: pretraining yields substantial latent ability, and post-training—especially RLHF—extracts and shapes it for interactive use, going beyond superficial style changes to influence reasoning and response quality. This book distills best practices and trade-offs across the pipeline, offers hands-on implementations, and situates RLHF within the larger post-training toolkit, preparing readers to navigate ongoing advances in areas like RLVR and reasoning-focused training.
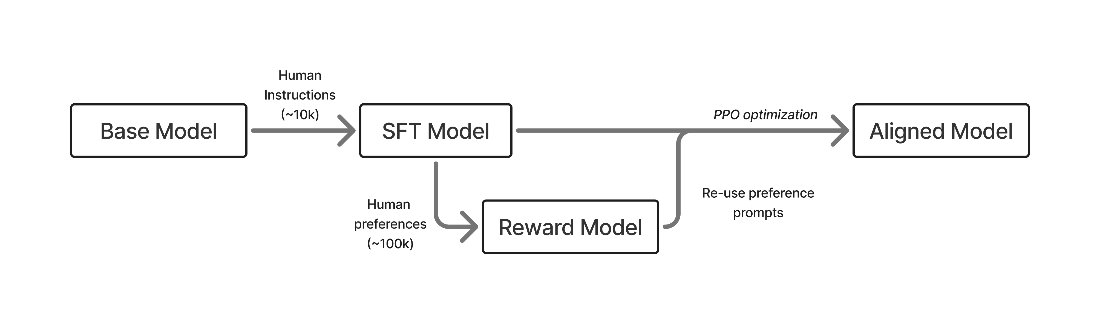
A rendition of the early, three stage RLHF process: first training via supervised fine-tuning (SFT, Chapter 4), building a reward model (RM, Chapter 5), and then optimizing with reinforcement learning (RL, Chapter 6).
Future of RLHF
With the investment in language modeling, many variations on the traditional RLHF methods emerged. RLHF colloquially has become synonymous with multiple overlapping approaches. RLHF is a subset of preference fine-tuning (PreFT) techniques, including Direct Alignment Algorithms (see Chapter 8), which are the class of methods downstream of DPO that solve the preference learning problem by taking gradient steps directly on preference data, rather than learning an intermediate reward model. RLHF is the tool most associated with rapid progress in “post-training” of language models, which encompasses all training after the large-scale autoregressive training on primarily web data. This textbook is a broad overview of RLHF and its directly neighboring methods, such as instruction tuning and other implementation details needed to set up a model for RLHF training.
As more successes of fine-tuning language models with RL emerge, such as OpenAI’s o1 reasoning models, RLHF will be seen as the bridge that enabled further investment of RL methods for fine-tuning large base models. At the same time, while the spotlight of focus may be more intense on the RL portion of RLHF in the near future – as a way to maximize performance on valuable tasks – the core of RLHF is that it is a lens for studying the grand problems facing modern forms of AI. How do we map the complexities of human values and objectives into systems we use on a regular basis? This book hopes to be the foundation of decades of research and lessons on these problems.
 The RLHF Book ebook for free
The RLHF Book ebook for free