1 Seeing inside the black box
Modern data science runs on powerful, convenient tools that can build impressive models with little friction, yet this convenience often masks a dangerous gap between usability and understanding. Algorithms now steer high‑stakes decisions in lending, healthcare, hiring, and justice; they perform well—until shifting conditions, hidden biases, fat‑tailed risks, or misaligned objectives expose their limits. The chapter argues that the critical skill today is not producing code, but cultivating clarity: seeing beyond polished outputs to the assumptions, trade‑offs, and vulnerabilities that shape every prediction, so we can explain decisions, question failures, and avoid blind trust in black boxes.
To reclaim that clarity, the book grounds modern practice in enduring ideas—from Bayes to Breiman and beyond—and introduces a “hidden stack” that traces how raw data, features, modeling choices, optimization goals, validation principles, and philosophical commitments interact. Models are not neutral machines; they embed beliefs about uncertainty, costs, evidence, and structure. Understanding this lineage yields practical leverage: choosing between interpretable and highly flexible classifiers, aligning thresholds with real costs, diagnosing data drift and leakage, and matching time‑series methods to assumptions about stationarity and noise. Foundations are presented not as nostalgia, but as mental models for making better design decisions under uncertainty.
The stakes are ethical as well as technical. Accountability requires interpretability; fairness demands scrutiny of proxies, class imbalances, and who benefits from a chosen loss. Automation through LLMs and AutoML accelerates workflows but can obscure objectives, defaults, and hidden constraints—turning experts into button‑pressers unless they can read, test, and justify the logic beneath the surface. The chapter sets expectations for the rest of the book: concept‑first explanations, light math, and historically informed insights that help readers diagnose, adapt, and defend models. By the end, the goal is not just to know how models work, but to understand why they work, when they fail, and how to see inside the black box with judgment and care.
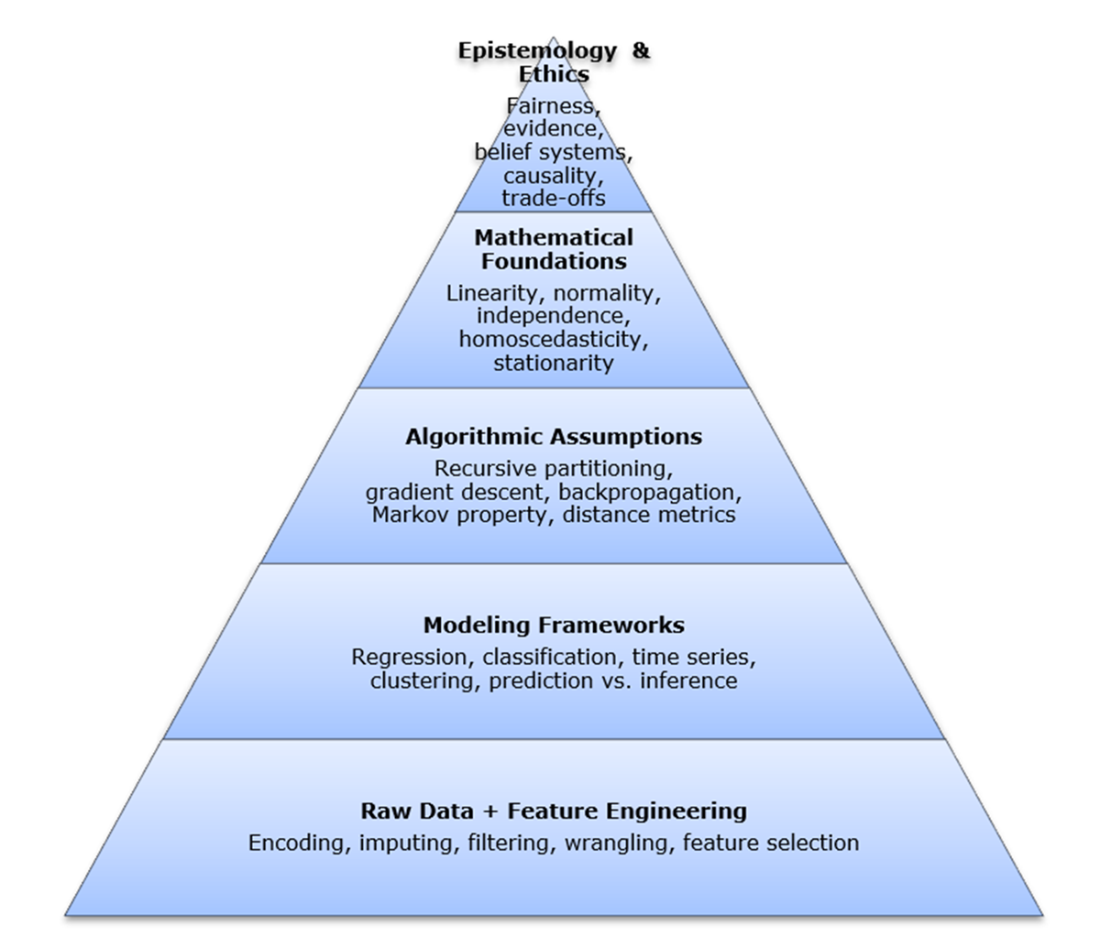
The hidden stack of modern intelligence. This conceptual diagram illustrates the layered structure beneath modern intelligence systems, from raw data to philosophical commitments. Each layer represents a critical aspect of data-driven reasoning: how we collect and shape inputs, structure problems, select and apply algorithms, validate results through mathematical principles, and interpret outputs through broader assumptions about knowledge and inference. While the remaining chapters in this book don’t map one-to-one with each layer, each foundational work illuminates important elements within or across them—revealing how core ideas continue to shape analytics, often invisibly.
Summary
- Interpretability is non-negotiable in high-stakes systems. When algorithms shape access to care, credit, freedom, or opportunity, technical accuracy alone is not enough. Practitioners must be able to justify model behavior, diagnose failure, and defend outcomes—especially when real lives are on the line.
- Automation without understanding is a recipe for blind trust. Tools like GPT and AutoML can generate usable models in seconds—but often without surfacing the logic beneath them. When assumptions go unchecked or objectives misalign with context, automation amplifies risk, not insight.
- Foundational works are more than history—they're toolkits for thought. The contributions of Bayes, Fisher, Shannon, Breiman, and others remain vital because they teach us how to think: how to reason under uncertainty, estimate responsibly, measure information, and question what algorithms really know.
- Assumptions are everywhere—and rarely visible. Every modeling decision, from threshold setting to variable selection, encodes a belief about the world. Foundational literacy helps practitioners uncover, test, and recalibrate those assumptions before they turn into liabilities.
- Modern models rest on layered conceptual scaffolding. This book introduces the “hidden stack” of modern intelligence, from raw data to philosophical stance—as a way to frame what lies beneath the surface. While each of the following chapters centers on a single foundational work, together they illuminate how deep principles continue to shape every layer of today’s analytical pipeline.
- Historical literacy is your best defense against brittle systems. In a field evolving faster than ever, foundational knowledge offers durability. It helps practitioners see beyond the hype, question defaults, and build systems that are not only powerful—but principled.
- The talent gap is real—and dangerous. As demand for data-driven systems has surged, the supply of deeply grounded practitioners has lagged behind. Too often, models are built by those trained to execute workflows but not to interrogate their assumptions, limitations, or risks. This mismatch leads to brittle systems, ethical blind spots, and costly surprises. This book is a direct response to that gap: it equips readers not just with technical fluency, but with the judgment, historical awareness, and conceptual depth that today’s data science demands.
 Timeless Algorithms: The Seminal Papers ebook for free
Timeless Algorithms: The Seminal Papers ebook for free